
Author: Weilin, PANews
In the Bitcoin decentralized finance (BTCFi) ecosystem, Core is a Bitcoin-driven, EVM-compatible L1 blockchain, with verification nodes maintained by miners, Bitcoin staking, and Core native token staking to maintain their security. Core, with its innovative Satoshi Plus consensus, combines Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), providing Bitcoin holders with long-term and robust income opportunities.
Currently, about 75% of the world's Bitcoin mining hash power has been contributed to Core's model through DPoW, and more than 9,000 Bitcoins have participated in its staking through non-custodial Bitcoin staking. Core is unlocking the potential of Bitcoin and making it the main protector and core asset of decentralized finance in the future.
On November 19, Core completed the Fusion upgrade and introduced two innovative products: Core Dual Staking and Core LstBTC. This article will analyze the important changes in this upgrade and explore the institutional adoption trend of BTCFi.
Deeply penetrate the Bitcoin community and innovatively launch the Satoshi Plus consensus
Core is based on its innovative Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, in which the DPoW mechanism allows Bitcoin miners to settle hash power on the Bitcoin mainnet through syntax such as OP_Return and delegate it to the preferred verification node to earn CORE token rewards. In this way, Core not only obtains the protection of Bitcoin miners, but also increases the income of miners, especially in the context of the reduction of Bitcoin block rewards, Core's block rewards make up for the reward vacancy after halving.
On the other hand, the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) in the Satoshi Plus consensus allows CORE token holders to support network security by delegating CORE to validation nodes. They can then participate in the election of these validators and receive CORE token rewards for securing the chain. The key to this mechanism is the "mixed score", which selects the top 27 validators by calculating the delegated hash and delegated stake, and is updated every 24 hours to ensure the decentralization and stability of the network.
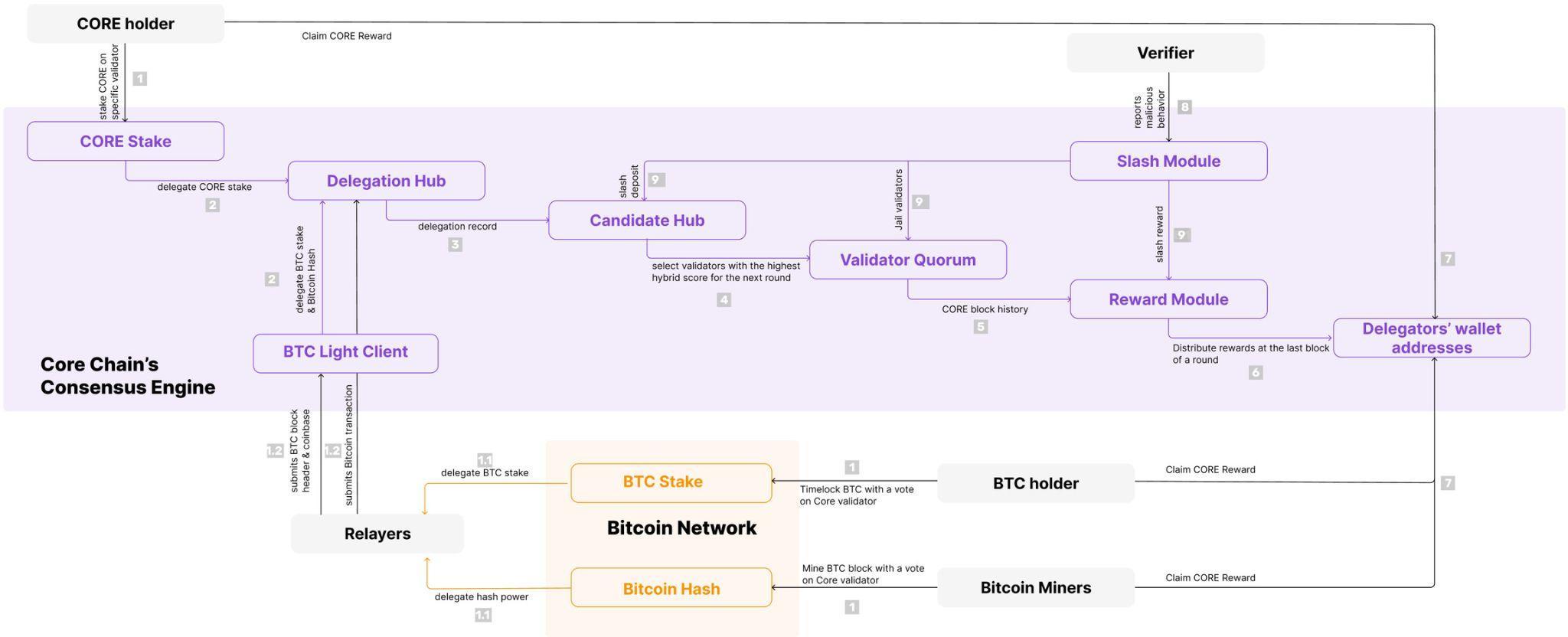
The third important component of the Satoshi Plus consensus is non-custodial Bitcoin staking, which has delegated more than 9,000 Bitcoin to Core blockchain validators since its launch in April 2024. The approach centers around absolute timelocks, a Bitcoin native feature that allows holders to lock their Bitcoin for a predefined period of time during which it cannot be spent. While Bitcoin remains locked on the Bitcoin blockchain, stakers delegate that Bitcoin to elect Core validators, who secure Core and are rewarded with CORE tokens. Through this process, Bitcoin holders are rewarded with CORE tokens every day without giving up custody of their assets or taking on counterparty risk.
It is worth noting that Core has deep connections with the Bitcoin community, especially miners and Bitcoin holders. This makes Core different from other Bitcoin L2 or sidechain projects. More than 75% of the global mining hash power provides support to the Core network through Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW), contributing computing power to the verification nodes on the chain, and then receiving security rewards. The zero-risk and asset-free nature of non-custodial Bitcoin staking has made many large Bitcoin holders and institutions willing to trust Core's technology and entrust their Bitcoin to verification nodes to maintain the security of the network. Unlike other Bitcoin projects, Core pays more attention to meeting their concerns about security and practical needs when providing Bitcoin holders with income opportunities.
Key points of Fusion upgrade: introduction of dual staking and LstBTC
In January this year, the Bitcoin spot ETF was approved, and in November the results of the US election were released. Subsequently, the cryptocurrency industry once again became a hot topic. The traditional financial community has been looking for more flexible ways to participate in Bitcoin.
In this context, Core further launched the Fusion upgrade on November 19. The Fusion upgrade enhances Core's BTCFi ecosystem through Core dual staking and LstBTC, and also provides institutions with a more efficient way to participate.
Among them, the launch of the double pledge product aims to solve the problem of balanced distribution of community rewards that may be caused by Bitcoin pledgers locking their assets and receiving CORE token rewards through verification nodes during the non-custodial pledge process. Especially when institutions pledge a large amount of Bitcoin, the released CORE rewards will increase accordingly. Based on this background, in order to encourage Bitcoin pledgers to re-stake the received CORE rewards to the verification nodes, double pledge increases user participation willingness by providing a higher annualized rate of return (APY). Double pledge is divided into four levels, and the profit ratio varies according to the ratio of the number of staked COREs to Bitcoin. They are Base, that is, 0 CORE: 1 BTC; Boost, that is, 1,000 CORE: 1 BTC; Super, that is, 3,000 CORE: 1 BTC; Satoshi, that is, 8,000 CORE: 1 BTC, this level will get the highest profit ratio.
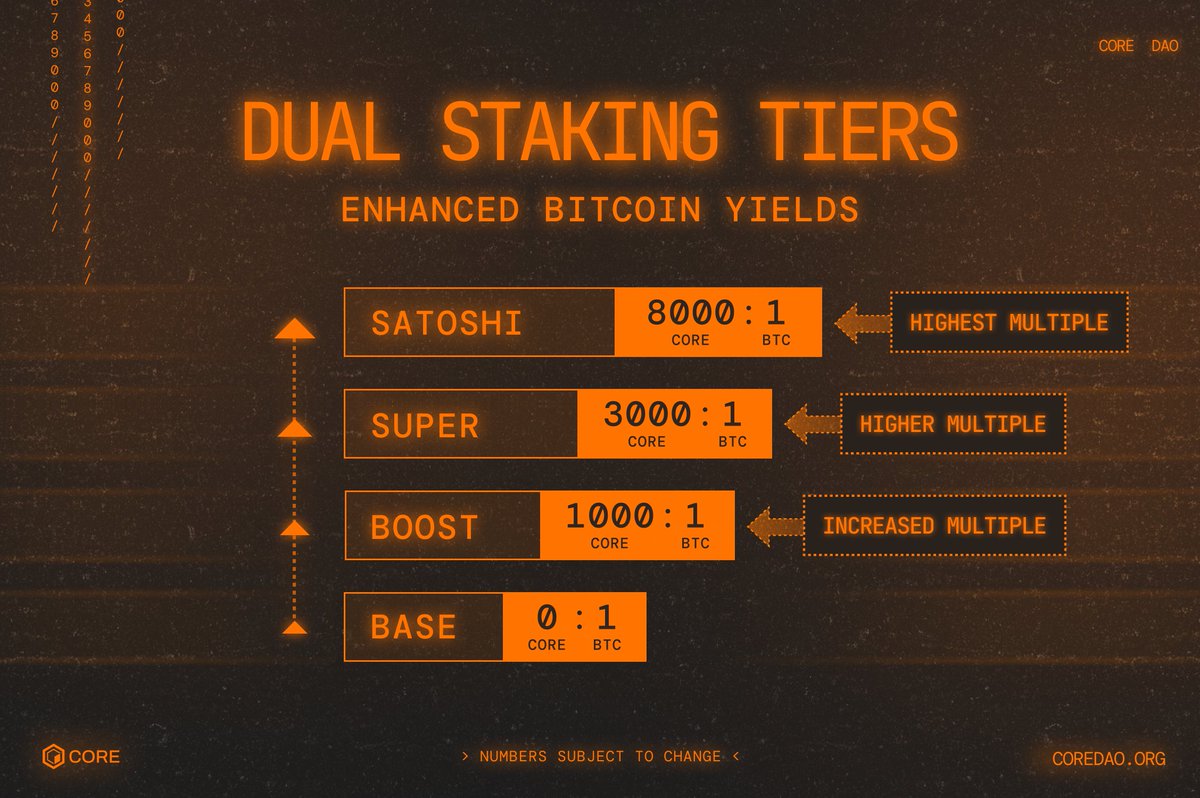
The basis for the dual staking operation is to further develop the non-custodial Bitcoin staking launched in April, allowing Bitcoin stakers to receive higher validation node rewards by staking CORE tokens. On the other hand, it also encourages CORE token holders to obtain higher staking rewards than single staking CORE tokens by holding and staking small amounts of Bitcoin (the minimum participation is 0.01 BTC). With the staking mechanism, Core has strengthened its alignment with Bitcoin, allowing many institutions to explore the possibility of Bitcoin income while maintaining the harmony between the security of the Core blockchain and the sustainability of income.
Overall, the Fusion upgrade has an important and beneficial impact on the entire Core ecosystem. Prior to the Fusion upgrade, delegated proof of work had attracted more than half of Bitcoin's total computing power. However, not all computing power delegators are clear about what to do with their CORE token rewards. Although CORE is the most useful token on the Core blockchain (used to pay gas fees, staking, and governance), miners often do not pay attention to non-mining activities. The CORE token introduced by the Fusion upgrade enhances the staking utility and can incentivize miners to stake their CORE rewards to earn returns on Bitcoin reserves.
Additionally, prior to the upgrade, Bitcoin stakers earned CORE tokens, which they could also stake, but CORE staking was separate from their primary Bitcoin staking interest. By double-staking to reward Bitcoin stakers who also stake CORE tokens, the economic value loop is closed and further aligns Bitcoin with CORE assets. This capability enhances Bitcoin stakers’ earnings and security commitment to Core.
Prior to Fusion, the three components of Satoshi Plus consensus operated largely in isolation, even as they closely tied miners and Bitcoin stakers to the Core community, but after double staking these components merged together to bring all stakeholders together in consensus around the Core network and the CORE token.
Another key part of this upgrade is LstBTC, which enables Bitcoin stakers to maintain their liquidity in the Core DeFi ecosystem while staking BTC. In addition, they will receive CORE tokens as rewards when staking. While earning Bitcoin staking income, users can use their LstBTC to borrow, exchange, re-stake, and participate in other on-chain activities.
There are more than 200 projects in the ecosystem, and institutional adoption is becoming a trend
With the continuous development of the Core network, more and more decentralized financial projects are being built on its platform. At present, the number of ecological projects on the Core chain has exceeded 200, including Pell Network, Solv Protocol, Avalon Finance, DeSyn Protocol, Colend, etc. The addition of these projects not only promotes the expansion of the Core ecosystem, but also provides impetus for the growth of its TVL (total value locked).
In 2024, the data on the Core chain has grown significantly: as of the third quarter, its TVL has increased by 614%, and the amount of Bitcoin and CORE tokens staked has increased by 85%. As of December 12, Core's TVL has exceeded US$983 million, with more than 31.5 million independent addresses on the chain and 327 million transactions completed.
Core's innovations have attracted not only Bitcoin holders, but also institutions. In June 2024, Core launched its first yield-based Bitcoin exchange-traded product (ETP), providing investors with the opportunity to earn returns through non-custodial Bitcoin staking. In partnership with Valour, a subsidiary of DeFi Technologies, this ETP offers investors a 5.65% yield, becoming an important way for institutional investors to enter the BTCFi ecosystem.
In addition, Core has established strategic partnerships with multiple custodians such as Fireblocks, Copper, Cactus, and Hashnote. These are all important service providers involved in Core's dual staking. One of the main reasons why custodians have become a key competitive field for Bitcoin staking protocols and the second layer is that most Bitcoin holders prefer to manage their assets through trusted custodians. These service providers usually provide zero-risk, stable income solutions, which is their primary consideration. Now, these service providers have become the institutional force for Core to unlock the potential of BTC.
It is worth mentioning that after the success of MicroStrategy's Bitcoin strategy, a large number of listed companies followed suit and bought Bitcoin and other crypto assets, while the listed company DeFi Technologies announced the launch of a strategy called CoreFi in November, further enhancing Core's appeal among institutional investors. The inspiration for the CoreFi strategy comes from the successful experience of MicroStrategy and Metaplanet. The CoreFi strategy provides investors with a regulated investment method to obtain leveraged Bitcoin and CORE income channels, allowing investors to obtain high-Beta Bitcoin and BTCFi economic exposure.
On December 9, the Core Foundation announced a partnership with BitGo, which became the first custodian to support users to participate in Core’s “double staking”. This partnership marks a further breakthrough for Core in terms of institutional adoption.
Through the Fusion upgrade, Core not only enhances the scalability and flexibility of the Bitcoin decentralized financial ecosystem, but also provides more profit opportunities for Bitcoin holders and institutions. The introduction of dual staking and LstBTC has made Core's position in the BTCFi field more solid.
In the future, with the launch of more innovative features and the growth of market demand, Core is expected to play a more important role in the Bitcoin ecosystem and become a bridge connecting Bitcoin holders with BTCFi. For investors, Core's innovation has brought new vitality to the market.














