Increasing TVL is the core goal of many DeFis and also the most critical issue.
There are four main methods:
1. Coin issuance expectations: Attract liquidity through points activities.
This method is the most direct and has the highest input-output ratio. It does not require any real money costs in the early stages, and you only need to give users future expectations.
It's like getting something for nothing.
There are two core groups in the cryptocurrency circle: those who speculate in cryptocurrencies and those who make money. These two groups correspond to the secondary market and the primary market respectively.
Those who speculate in cryptocurrencies are secondary market users, making money through trading; those who profit from the profits are primary market users, who participate in projects at an early stage, contribute data to the projects, and obtain airdrop shares when tokens are issued.
Well, for projects that have not yet issued coins, a very good marketing method is to organize various airdrop activities.
By giving early users points as rewards, they are attracted to participate, and users are given the expectation that points can be exchanged for platform tokens or other rewards. This method can attract users and build a community before there is any substantial capital expenditure.
2. Cooperation with other projects: Through cooperation with different projects, the interoperability and liquidity of assets can be achieved.
This method is more dependent on the project’s own background and channels, and its essence is resource exchange.
For example, users can use tokens from other projects as collateral or a means of payment on your platform.
Typical examples are Merlin and Solv. After the Bitcoin L2 Merlin was launched, in order to keep liquidity in its own ecosystem, it cooperated with the Bitcoin staking protocol Solv and imported liquidity into Solv. Solv then became the largest Bitcoin staking protocol.
Of course, Solv currently only supports Merlin, the Bitcoin L2, so the liquidity remains in Merlin. This is the cost paid by Solv, and it is ultimately a disguised win-win situation.
3. Income incentives: The typical approach is liquidity mining, setting up a liquidity pool, and attracting users to add assets to the liquidity pool through transaction fee rewards.
This is a very popular incentive mechanism where users provide liquidity to a designated pool and receive rewards. This method can quickly increase TVL.
This approach requires the design of a reasonable reward mechanism to avoid inflation caused by excessive rewards, while also paying attention to risk management.
4. Create more new assets: Liquidity staking and liquidity re-staking are creating new assets, thereby attracting incremental funds.
Issuing new assets is not just to release the liquidity of already pledged assets, but more importantly, it can attract incremental funds. By creating new financial instruments such as stETH (pledged ETH certificates), not only does it improve the liquidity of already pledged assets, it also creates new investment opportunities and attracts more capital.
Of course, the risk is the accumulation of risks brought about by the layers of nesting dolls.
Once the token of one of the links explodes, the related assets and applications upstream and downstream of this token will have problems.
For example, if stETH explodes, not only will the stability of the upstream Ethereum PoS mechanism be greatly affected, but also various downstream re-pledge protocols that accept stETH assets, such as Eigenlayer, will be at risk.
To summarize, the costs, benefits, and risks of the four methods are listed as follows:
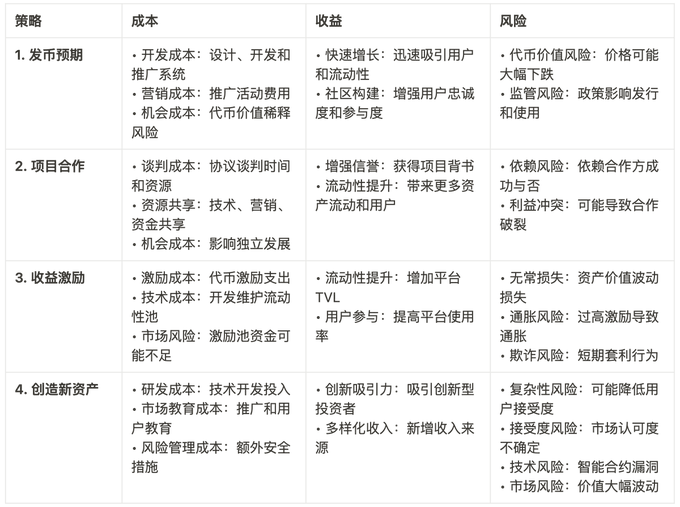
If we must rank the four methods in order to maximize capital efficiency from the perspective of the project owner, the order is as follows:
Coin issuance expectations: low cost and high returns;
Second, project cooperation: the cost is not high, just exchange resources;
The third benefit incentive is that the cost is high and you need to pay real money to share the platform benefits;
Creating new assets 4: The cost is the highest, and the liquidity of new assets needs to be maintained;
But this prioritization is based on the assumption that projects want to quickly establish market position and attract users while managing risks and maintaining efficient use of resources.
In practice, project owners need to adjust these priorities based on their own resources, market conditions, and specific business goals.
In addition, these methods are not mutually exclusive, and project owners can combine these strategies based on the needs and market feedback at different stages.












