This research report, co-authored by Standard Chartered Bank and Synpulse, is a comprehensive report on the tokenization of real-world assets in cross-border trade scenarios. The report details how tokenization will become a game-changer in global trade, providing investors with unprecedented liquidity, divisibility and accessibility by converting trade assets into transferable instruments.
Traditional financial assets are subject to huge fluctuations due to macro market influences, but trade assets are different. Although trade is closely related to the economy, economic recession will have an impact on bank loans. However, the huge trade financing gap still provides a good opportunity for investors to enter the market, because even during the economic slowdown, small and medium-sized enterprises still need a lot of financing, thus creating continuous investment opportunities. To some extent, trade assets can resist the global economic recession.
At the same time, we believe that this type of trade asset is more suitable as a tokenized underlying asset due to its relatively short cycle, low default rate, and large financing demand. In addition, the tokenization of trade assets can also provide many benefits to various participants and process links in the complex process of global trade, whether in 1) payment of cross-border trade, 2) financing needs between various trade participants, and 3) using smart contracts to improve trade efficiency, reduce complexity, and make it more open and transparent.
Standard Chartered Bank predicts that by 2034, the overall demand for tokenization of real-world assets will reach US$30.1 trillion, of which trade assets will become the top three tokenized assets and will account for 16% of the total tokenization market in the next decade.
Therefore, we compiled this report into a document to provide reference for market participants and investors. The article explores the transformative power of trade asset tokenization and shares why now is the perfect time to adopt and expand trade asset tokenization. At the same time, it also examines the four key benefits of embracing tokenization and proposes actions that investors, banks, governments and regulators can take now to capture this opportunity and shape the journey to the next chapter of finance.
Enjoy the following:

Tokenization of Real-World Assets: A Game Changer for Global Trade
Over the past year, we have witnessed rapid development of tokenization, which reflects a significant shift towards a more accessible, efficient and inclusive financial system. In particular, asset tokenization of trade assets represents both a shift in our understanding of value and ownership, and a fundamental change in investment and exchange mechanisms.
Standard Chartered’s successful pilot in Project Guardian, led by the Monetary Authority of Singapore, demonstrated the viability of asset tokenization as an innovative “origin to distribution” structure and the potential opportunities it presents for investors to participate in financing real-world economic activities.
Standard Chartered has taken this vision a step further with Project Guardian, pioneering an initial token offering platform for real-world assets. They successfully simulated the issuance of $500 million in asset-backed securities (ABS) tokens backed by trade finance assets on the public Ethereum blockchain.
The success of this project demonstrates how open and interoperable networks can be used in practice to facilitate access to decentralized applications, stimulate innovation, and promote growth within the digital asset ecosystem. This pilot project demonstrates the practical application potential of blockchain technology in the financial sector, especially in improving asset liquidity, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing market access and transparency. Through tokenization, trade assets can be accessed and traded more efficiently by global investors, transforming trade assets into transferable instruments, and unlocking previously unimaginable levels of liquidity, divisibility, and accessibility. It not only provides investors with a new opportunity to balance their portfolios through digital tokens with traceable intrinsic value, but can also help narrow the global $2.5 trillion trade finance gap.
1. What is asset tokenization?
As the financial world undergoes rapid digitization, digital assets are at the forefront, revolutionizing the way we view and exchange assets. Traditional finance, combined with innovative blockchain technology, will lead a new era of digital finance, fundamentally reshaping our understanding of value and ownership.
Before 2009, the idea of transferring value through digital assets was still unthinkable. The exchange of value in the digital realm still relies on intermediaries, acting as gatekeepers and creating inefficient processes. Although there is debate in the financial industry over the precise definition of digital assets, it is undeniable that they are ubiquitous in our technology-driven lives. From the information-rich digital files we use daily to the content we consume on social media, they permeate every corner of our modern existence.
The introduction of blockchain technology has been a game changer. It is revolutionizing the financial markets. What was once unthinkable is becoming a reality, and tokenization has become a key element in expanding the digital asset market, transforming it from niche and experimental to widely accepted and mainstream.
“Tokenization” essentially refers to the process of issuing digital representations of traditional assets in the form of tokens on a distributed ledger.
Tokenization refers to the process of issuing digital representations of real or traditional assets in the form of a token on a distributed ledger.
These tokens are essentially digital certificates of ownership that increase operational efficiency and automation. Notably, it is closely related to the concept of fragmentation, where a single asset can be divided into smaller transferable units. But the most revolutionary aspect is that tokenization enhances access to new asset classes and improves financial market infrastructure, opening the door to innovative applications and entirely new business models in decentralized finance (DeFi).

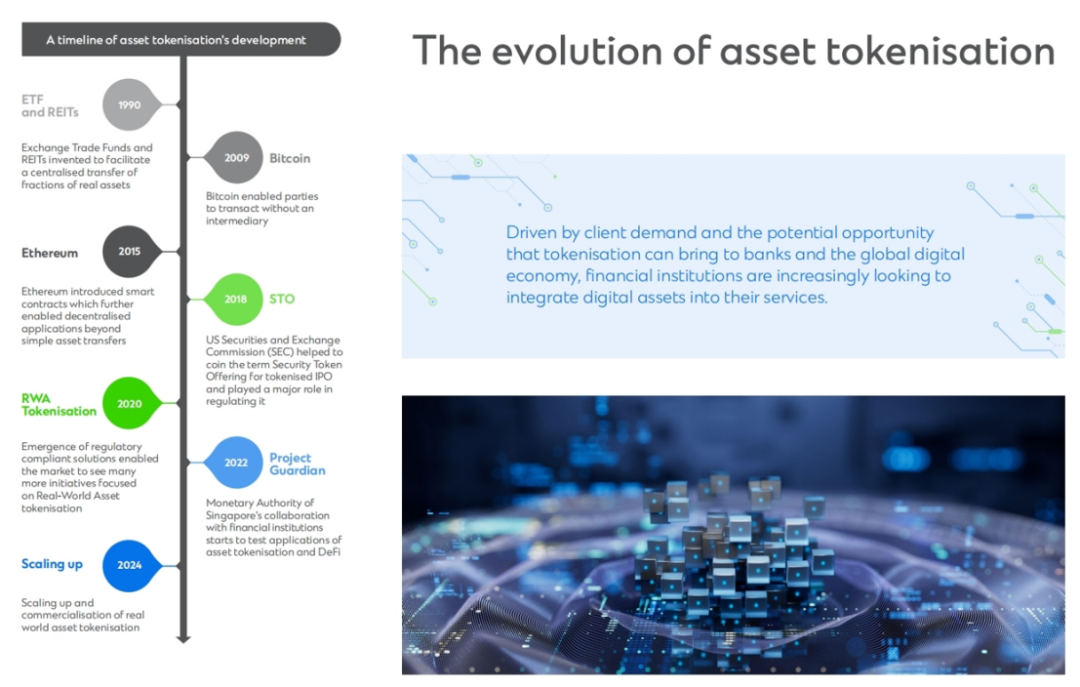
2. Development of Tokenization
Tokenization dates back to the early 1990s. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) were the first to enable decentralized ownership of physical assets, allowing investors to own a portion of a physical asset such as a building or commodity.
Until 2009, the world witnessed the birth of Bitcoin, a digital currency that challenged the concept of traditional third-party intermediaries. It triggered a revolution, and then Ethereum came into the limelight in 2015. Ethereum is a pioneering software platform driven by blockchain technology, which introduced smart contracts that support the tokenization of any asset. It laid the foundation for the creation of thousands of tokens representing various assets, such as cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, security tokens, and even non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which demonstrated the possible use of tokenization in representing digital and physical items.
The following years saw the emergence of a host of new phenomena: Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs) and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) coined the term “Securities Token Offerings (STOs)” in 2018, paving the way for regulated tokenized offerings and giving rise to regulatory compliant solutions.
These developments have paved the way for the tokenization of real-world assets to take the main stage. They continue to act as a catalyst for change and technological improvements in the financial services sector, paving the way for continued new applications. The financial services industry continues to actively explore the potential of tokenization. Driven by customer demand and the potential opportunities that tokenization brings to banks and the global digital economy, financial institutions are increasingly looking to integrate digital assets into their services.
A prime example of such an initiative is Project Guardian, an industry-wide collaboration between the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and industry leaders to test the feasibility of asset tokenization and DeFi applications. These industry pilots will further reveal the opportunities and risks arising from the rapid innovation of digital financial tokenization.
Case A: Project Guardian Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) Tokenization Project
Standard Chartered Bank has demonstrated a bold vision in Project Guardian: how blockchain networks can be used to advance the development of safer and more efficient financial networks. This is a collaboration between MAS and industry leaders, with participating institutions conducting market case studies and designing a blueprint for future market infrastructure that leverages the innovative potential of blockchain and DeFi.
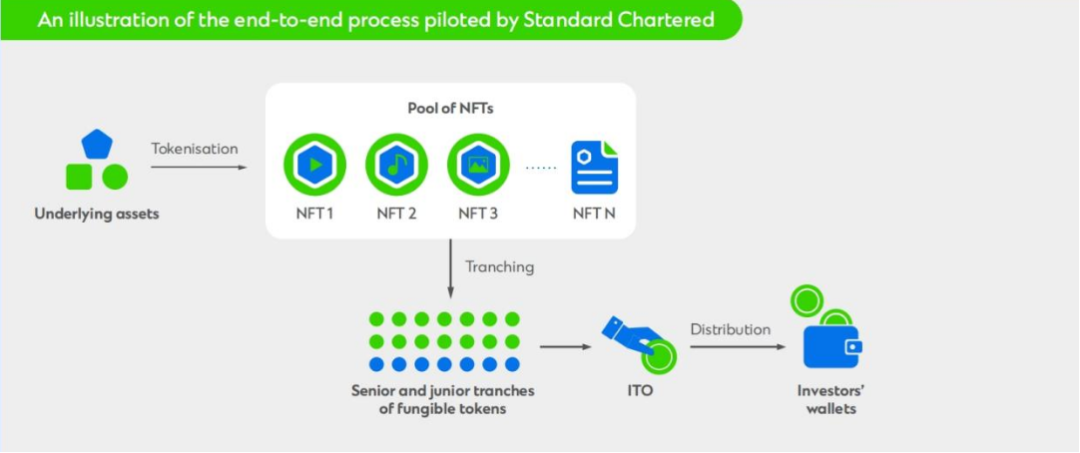
Standard Chartered has taken this vision a step further by pioneering a token issuance platform for real-world assets, successfully simulating the issuance of $500 million of asset-backed securities (ABS) tokens backed by trade finance assets on the public blockchain Ethereum. Through this initiative, Standard Chartered tested the end-to-end process from origination to distribution, including simulating default scenarios.
- Tokenization: Trade finance receivables assets are tokenized in the form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
- Risk-based Allocation: These NFTs are structured (Senior and Junior Tranche) based on the expected risks and returns to ensure strict cash flow allocation.
- Fungible Token Creation: Based on the NFT of the underlying assets and the structured design, two types of FT tokens are created. Senior FT tokens provide a fixed rate of return, while secondary FTs provide excess spreads.
- Distribution and access: Finally, these tokens are distributed to investors through the ITO.
The Project Guardian pilot successfully demonstrated how to use open and interoperable blockchain networks in practice to facilitate access to decentralized applications, stimulate innovation and promote the growth of the digital asset ecosystem. The application scenarios can be expanded to include tokenization of financial assets such as fixed income, foreign exchange and asset management products, which can achieve seamless cross-border trading, distribution and settlement.
At the same time, by tokenizing financing needs in cross-border trade scenarios, this new digital asset class is introduced to a wider group of investors and helps improve liquidity in the trade finance market.
3. What else can we see besides the tokenization of trade assets?
Tokenization not only creates a new way to invest in digital assets and brings much-needed transparency and efficiency to trade finance, it also enables deeper participation in trade finance and simplifies the complexity of supply chain finance.
Credit Transmission: Typically, trade finance is only available to established first-tier suppliers, while deeper suppliers – smaller, often lacking scale, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the supply chain – are often excluded from trade finance. Through tokenization, the overall resilience and liquidity of the supply chain can be increased by enabling SMEs to rely on the credit rating of an anchor buyer.
Liquidity Creation: Tokenization is often touted as unlocking huge potential, especially in inefficient and illiquid markets. A consensus is emerging that investors are inclined to adopt tokenized assets due to reduced transaction costs and enhanced liquidity. For institutions on the supply side, the attraction seems to be access to new capital, increased liquidity, and streamlined operational efficiencies.
Beyond that, Standard Chartered Bank believes that the real transformative power of tokenization is much greater. The next three years will be a critical node for tokenization, new asset classes will be tokenized rapidly, and trade finance assets will take center stage as a new asset class. Industry development is reaching a new level, and public utilities will reap more rewards than isolated efforts.
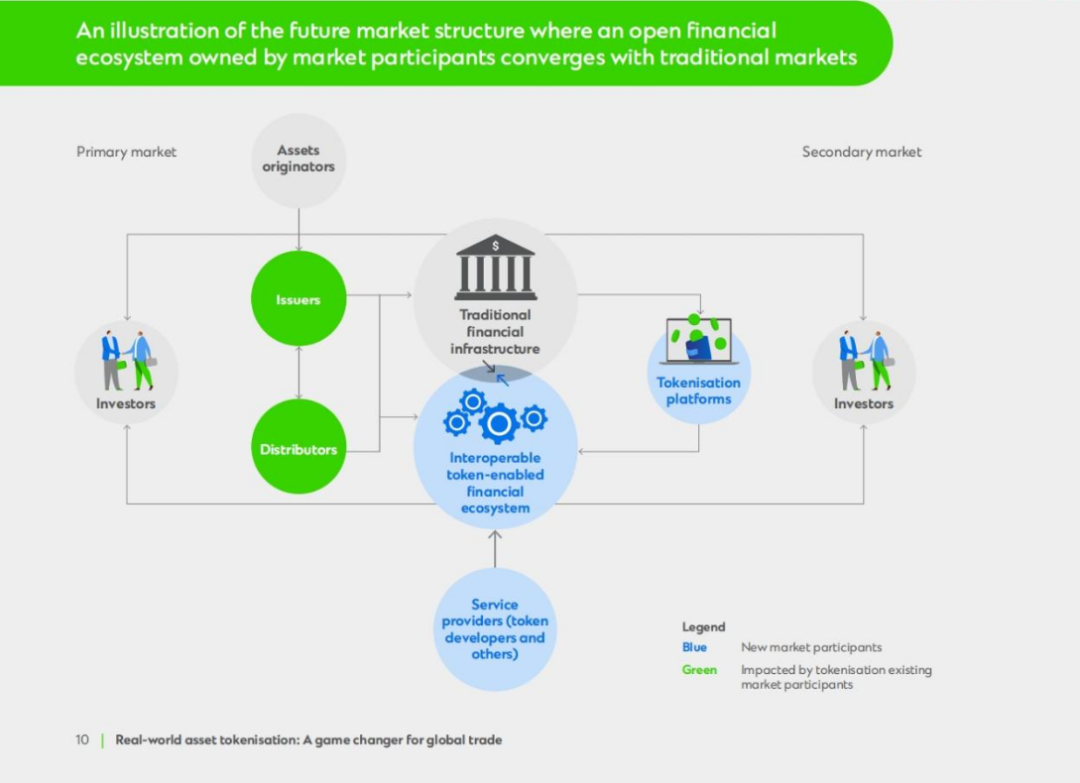
To provide access to new asset classes, banks play a key role in providing trust and connecting existing traditional financial markets with new, more open, token-backed market infrastructure. Maintaining a position of trust is fundamental to verifying the identities of issuers and investors, running KYC/AML checks and granting credentials to participate in this new interoperable financial ecosystem.
Standard Chartered Bank envisions a future where traditional and tokenized markets coexist and eventually merge, which urgently requires an open and permissioned multi-asset and multi-currency digital asset infrastructure to complement traditional markets. Compared with the closed-loop markets of the past, ownership and utility are shared by a wider range of market participants, striking a balance between inclusiveness and security. Such an infrastructure will not only promote efficiency and innovation, but also solve the current pain points of the industry, such as duplicate investment and isolated, fragmented development, which hinder growth and cooperation.
4. What drives the tokenization of trade assets?
The current macro and banking environment serves as a catalyst for adoption as tokenization brings unprecedented liquidity, divisibility, and accessibility to an asset class that has been viewed as complex over the past decade.
4.1 SMEs: Unlocking a multi-trillion dollar opportunity to bridge the trade finance gap
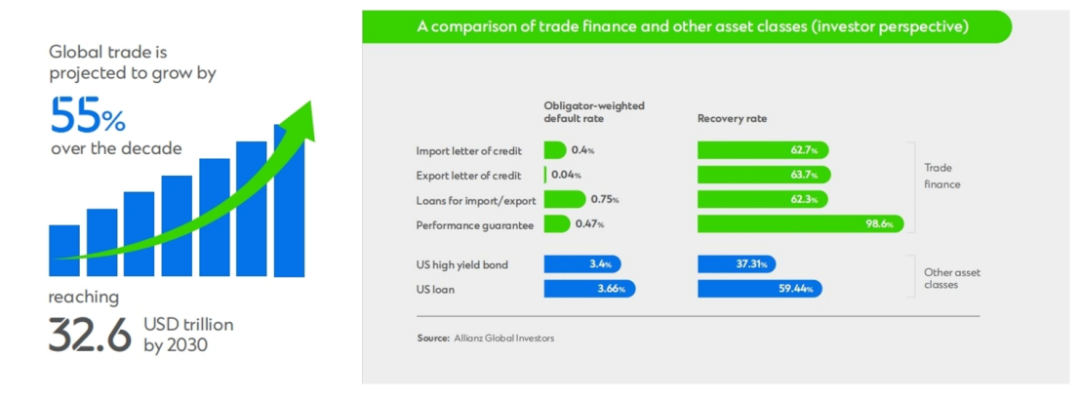
Standard Chartered Bank expects global trade to grow 55% over the next decade, reaching $32.6 trillion by 2030. Digitalization, expanded global trade, increased market competition and improved inventory management are factors driving this expansion. However, there is a huge gap between the demand and supply of trade finance, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises in developing countries.
The trade finance gap has been increasing dramatically – from $1.7 trillion in 2020 to $2.5 trillion in 2023. This increase represents a 47% lift in demand. This is the largest single-period increase since the indicator was launched, as a combination of factors including COVID-19, economic difficulties and political instability make it more difficult for banks to approve trade finance.
Furthermore, the International Finance Corporation (IFC) estimates that 65 million businesses in developing countries, representing 40% of formal micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), have unmet financing needs. While the plight of SMEs and MSMEs is widely acknowledged, one key segment remains under-recognized: the “missing middle”.
The “missing middle” or middle market companies (SMEs) are a difficult group for investors to access. SMEs sit between large investment grade corporates and smaller retail and SMEs and are particularly active in fast-growing regions such as the Middle East, Asia and Africa. They represent a large and untapped market that presents significant opportunities for investors.
This investment opportunity is also recession-proof. Since trade is closely linked to the economy, a recession will have an impact on bank lending. However, the large trade gap provides a good opportunity for investors to enter the market because even during an economic slowdown, small and medium-sized enterprises still require a lot of financing, creating continuous investment opportunities.
It is also worth noting that according to the Asian Development Bank, the $2.5 trillion global trade finance gap represents 10% of all traded exports. As current trade finance covers 80% of all exports today, the other 10% could represent an additional undisclosed trade finance gap as companies either do not seek such financing or are unable to access it. This means that the total current undisclosed trade finance gap could amount to a potential total opportunity of $5 trillion.
4.2 The Profitable Market that Has Not Yet Been Exploited by Investors
Trade finance assets are attractive but underinvested. They generate strong risk-adjusted returns and have some unique characteristics:
- Allows for risk diversification. Trading assets are short-lived, self-liquidating, and considered low-risk investments, with relatively low correlations to the stock and bond markets. This makes them a more stable asset class while still providing strong risk-adjusted returns.
- Broad investment scope. There is a wide variety of trading assets to choose from to suit investors’ specific risk appetite. Together with less accessible emerging and frontier markets such as Ghana, Cote d’Ivoire, Bangladesh or Saudi Arabia, this asset class can cater to a wide range of investors.
- Low default risk and high recovery rates. Most importantly, trade finance assets have an impressive track record. Compared to public credit, trade finance has relatively low default rates and higher recovery rates in the event of default, which strongly suggests that trade assets offer better risk-adjusted returns than other debt instruments.
While institutional investors underinvest in such assets due to lack of understanding, inconsistent pricing, lack of transparency, and operational intensity, tokenization can help address this issue.
4.3 Banks are incentivized to adopt tokenization and leverage blockchain-based digital origination distribution models to unlock capital in frontier markets
Basel IV is a comprehensive set of measures that will have a significant impact on the way banks calculate risk-weighted assets. Although full adoption is not expected until 2025, banks will need to develop growth strategies under Basel IV by modernizing their distribution business models.
Through blockchain-based origination distribution, banks can de-recognize assets from their balance sheets, thereby reducing regulatory capital to cover risk and helping to promote efficient asset origination. Banks can leverage tokenization by distributing trade finance instruments to capital markets and emerging digital asset markets. This "digital origination distribution" strategy for their trade finance assets can enable banks to improve return on equity, expand funding sources, and increase net interest income.
The global trade finance market is large and ripe for tokenization. Most trade finance assets held between banks can be tokenized and converted into digital tokens, allowing global investors seeking returns to participate.
4.4 Realistic Demand Promotes Growth
According to a report by EY Parthenon, demand for tokenized investments will soar, with 69% of buy-side firms planning to invest in tokenized assets by 2024, up from 10% in 2023. Furthermore, by 2024, investors plan to allocate 6% of their portfolios to tokenized assets, rising to 9% by 2027. Tokenization is not a fleeting trend; it is a fundamental shift in investor preferences.
However, the supply side of the market is still in its infancy, with the total value of real-world asset tokenization (excluding stablecoins) estimated to be around $5 billion by early 2024, primarily in commodities, private credit, and U.S. Treasuries. In contrast, Synpulse estimates that the addressable size, including the trade finance gap, will be $14 trillion.
Based on current market trends, Standard Chartered Bank expects that by 2034, the overall demand for real-world asset tokenization will reach $30.1 trillion, of which trade finance assets will become the top three tokenized assets and account for 16% of the total tokenization market in the next decade. As demand is likely to exceed supply in the next few years, it has the potential to help solve the current $2.5 trillion trade finance gap.

5. Four benefits of embracing tokenization
Asset tokenization has the potential to transform the financial landscape, providing increased liquidity, transparency, and accessibility. While it holds great promise for all market participants, realizing its full potential requires the concerted efforts of all stakeholders.
Trade finance stimulates the global economy, but traditionally, such assets have been sold primarily to banks. Tokenization opens the door to a wider group of investors and usher in a new era of growth and efficiency.
5.1 Improving market access
Today, institutional investors are eager to enter new, fast-growing markets. Emerging markets can be an attractive option for diversifying investments. However, investors are unable to fully exploit the opportunities offered by emerging markets due to the lack of necessary local expertise and effective distribution networks.
This is where tokenization comes in handy. By distributing trade finance assets through digital tokens, banks can increase net interest income and optimize capital structure, while investors, businesses and communities that rely on trade finance can benefit through improved accessibility. A closer look at Standard Chartered and the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s early collaboration on Project Guardian highlights the transformative power of tokenization. The pilot demonstrated how an open, interoperable digital asset network can unlock market access and allow investors from different ecosystems to participate in this tokenized economy, paving the way for more inclusive growth.
5.2 Simplifying trade complexity
Trade finance is often viewed as a complex scenario due to the multi-party and cross-border nature of global capital and goods trade flows. This asset class is less standardized, with varying sizes, timings and underlying commodities, making it difficult to invest in large volumes.
Tokenization provides a platform that can address this complexity.
Tokenization is more than just a new way to access investment, it is also an enabler for deep financing. Typically, trade finance is only available to established tier-one suppliers, while “deep tier” suppliers are often excluded from trade finance. As a solution, token-backed deep tier supply chain financing can remove the complexity.
In addition to bringing much-needed transparency and efficiency to trade finance, tokenization can also improve the overall resilience and liquidity of supply chains by enabling SMEs to rely on the credit rating of anchor buyers.
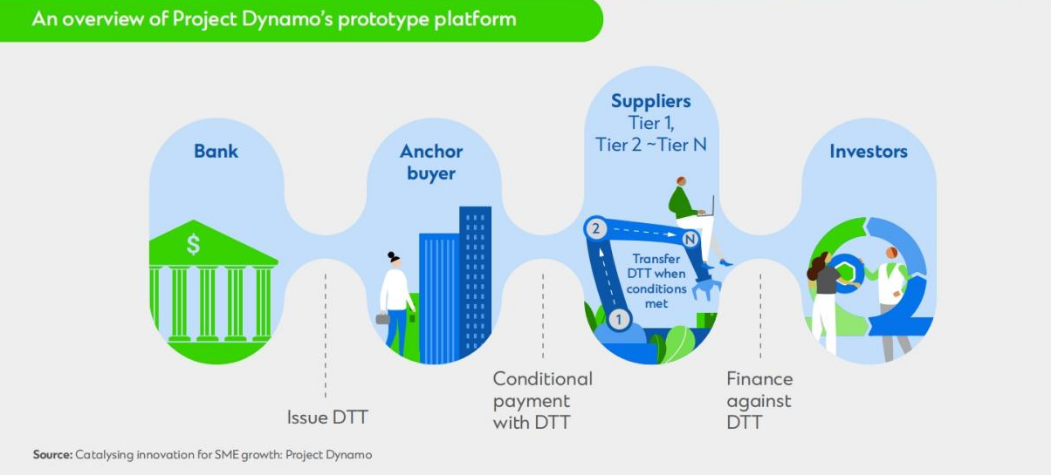
Case B: Project Dynamo: Solving trade complexity with digital trade tokens
Project Dynamo, a collaboration between Standard Chartered, the BIS Hong Kong Innovation Hub, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and technology companies, is a prime example of how digital trade tokens can be used to address trade complexities.
This collaborative effort has resulted in the development of a prototype platform where major buyers use tokens to make programmable payments to suppliers across their supply chain. Smart contract technology is used to automatically execute and redeem these tokens based on specific events (such as conditions that trigger eBL or ESG), enabling efficient and transparent trade processes. Major buyers can also use tokens to make conditional payments to their SME suppliers, and the tokens will only be converted into cash when pre-set conditions (such as proof of delivery or electronic bill of lading) are met.
Token holders also have multiple options for handling their tokens. They can hold the tokens, sell them to obtain financing, or use them as collateral for a loan. Transferring ownership through tokenization gives deep layer providers greater flexibility in managing their funds efficiently.
The benefits are not limited to individual participants either. Digital transaction tokens are issued in the form of “stablecoins” and are backed by dedicated bank funds or bank guarantees. Coupled with the programmability and transferability provided by blockchain infrastructure, institutional investors are gaining confidence in investing in small and medium-sized enterprises and supply chain financing (areas previously seen as high-risk).
Project Dynamo is just the beginning. It lays out a blueprint to address the difficulties suppliers, especially SMEs, face in accessing deep supplier finance by providing more adaptable and efficient financing and payment options. Ultimately, it creates a new avenue of financing for those who previously could not access traditional financing options.
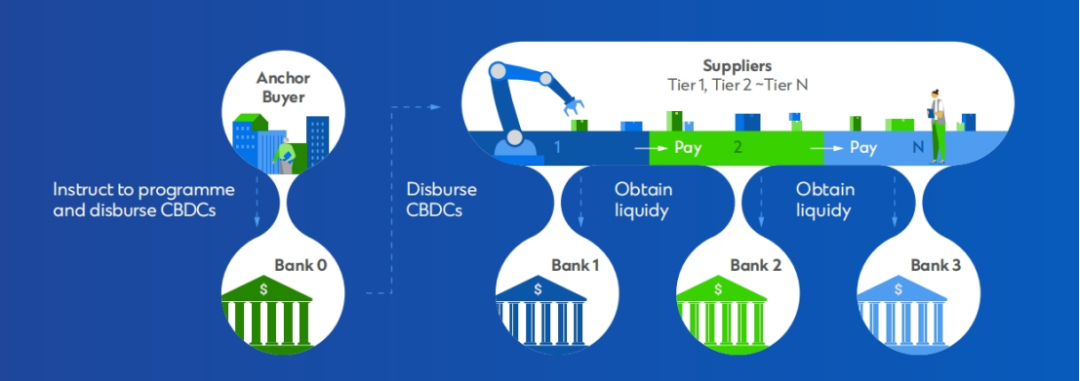
Case C: Leveraging CBDC’s programmability to optimize trade processes/financing
While tokenization brings exciting possibilities for addressing the complexity of the trade ecosystem, the programmability of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) also brings another game-changer. These digital versions of fiat currencies issued by central banks can enable programmable transactions using the self-executing capabilities of smart contracts, further streamlining the process of trade and supply chain financing.
Imagine a scenario where a large company with a good credit record (anchor buyer) has a network of suppliers, many of which are small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with little access to credit. With a programmable CBDC, the anchor buyer can instruct its bank to program future CBDC payables and distribute them directly to suppliers, who can then use them to improve operating capital efficiency or pay suppliers at the next level.
This streamlined process offers numerous advantages for deep supply chain financing:
- Enhanced Flexibility: Deep-seated providers can leverage digital currencies as collateral to borrow fiat currencies, unlocking new financing options and increasing operational flexibility.
- Smoother credit assessment: Banks can leverage customer information collected through payment data to streamline the SME credit assessment process and reduce the operational costs and risks banks face when collecting data.
- Scalability and transparency: CBDC makes SME operations more scalable and easier for all parties along the supply chain to report on ESG management and sustainability.
- Stability and confidence: More broadly, CBDCs enhance stability and transparency across the supply chain.
In the above scenarios, smart contracts play a vital role in helping to automate payment and financing processes:
Pre-Defined Contract: By leveraging smart contracts, CBDC can be programmed and combine payment and trade information to become a new trade financing tool.
Purpose-Bound Payment: Deep suppliers who do not meet credit requirements can use tokens as collateral to obtain financing related to the purpose of issuance.
Purpose-Bound Financing: This type of CBDC can be transferred by anchor buyers to their suppliers, who can immediately use it as a form of payment to deeper suppliers.
Obligation Fulfilment: Once the conditions in the smart contract are met, the smart contract will execute itself and the CBDC restrictions will be automatically lifted.
5.3 Digital Securitization
While traditional finance’s securitization of trade assets into financial products is effective, it only applies to a limited subset of assets, such as working capital loans and import/export financing assets. Tokenization will greatly expand this set of investable assets.
Due to the short-lived nature of trade assets, the entire process is operationally inefficient and the trade asset class requires a comprehensive management solution in order to track the underlying assets, assess performance and determine funding and payments.
These can all be solved through tokenization and the programmability of smart contracts, with AI automating the complexity and diversity behind the scenes. By automating processes, data management can be simplified and automated. Each token is traceable because it is associated with an account receivable. This helps with status monitoring, minimizes manual errors, facilitates transparency for all parties involved, and supports the assessment of accounts receivable and financing amounts.
Programmability also simplifies the transfer of ownership during transactions and improves transaction efficiency.
Since tokenization involves a standardized representation of accounts receivable, it creates a common language that can make the management of accounts receivable across jurisdictions more straightforward.
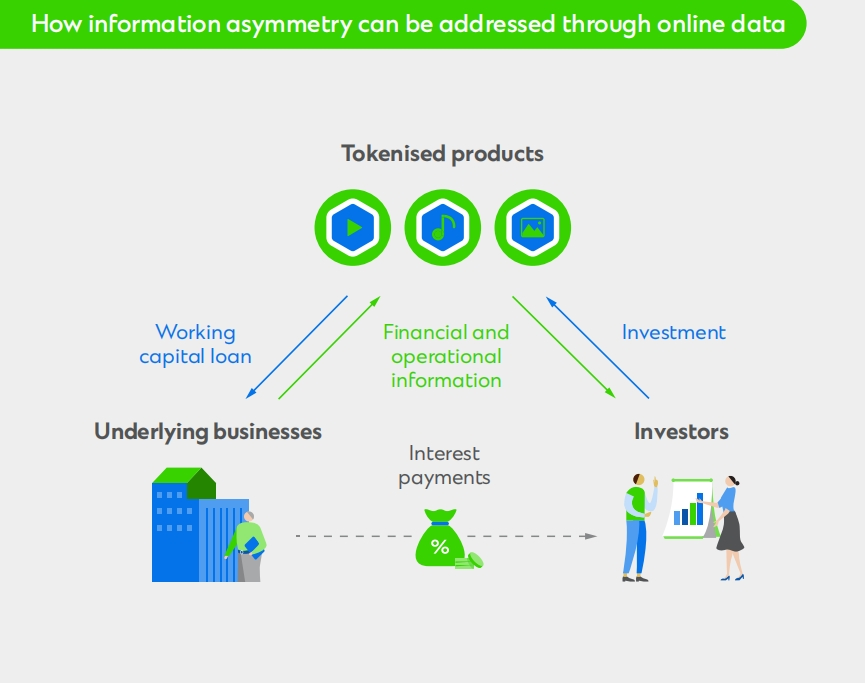
5.4 Reducing Information Asymmetry
Using blockchain to trace the underlying underlying assets helps reduce information asymmetry between issuers and investors, thereby enhancing investor confidence.
Developing a listing framework for tokenized assets is an important step in encouraging adoption and increasing investor confidence, and publicly disclosing offering documents makes it easier for investors to obtain relevant information needed for due diligence. Listing tokens can also ensure that issuers have a certain level of transparency and ensure that regulatory disclosure requirements are met, which is critical for many institutional investors.
Today’s investors are more sophisticated and demand greater transparency and control. We will soon see tokenized products emerge as a new way to reduce information asymmetry. In addition to representing the underlying asset, tokens can also contain other functions, including providing online access to operational and strategic data from said assets. For example, in the tokenization of a working capital loan, investors can access the operating parameters of the underlying business, such as profit margins or the number of leads in the sales pipeline. This model has the potential to increase investment returns and bring transparency to a new level.
6. How to participate in the tokenization market?
Asset tokenization has the potential to transform the financial landscape, providing greater liquidity, transparency, and accessibility. While it holds promise for all market participants, realizing its full potential requires the concerted efforts of all stakeholders.
6.1 Adoption
For institutional investors seeking to gain access to new asset classes or enhance returns, tokenization can provide more specific and differentiated solutions that meet the specific risk-return profiles and liquidity preferences of their clients.
Family offices and high net worth individuals (HNWIs) can benefit from a more efficient way to grow their wealth through diversification and transparent product structures, unlocking previously inaccessible opportunities.
To seize this investment opportunity, investors should start with a solid foundation. Since this is a new and evolving field, understanding new risks is critical, so start with education to build expertise.
For example, participating in pilot programs will enable investors and asset managers to experiment and build confidence in allocating to tokenized assets.
7.2 Cooperation
The industry is at a tipping point to fully embrace asset tokenization. Market-wide collaboration is essential to realize the benefits of tokenization. Overcoming distribution challenges and achieving better capital efficiency requires collaborative efforts. Banks and financial institutions can expand their reach through collaborative business models, such as developing the industry utility of tokenization. Similarly, intermediaries such as insurance companies can serve as alternative distribution channels, expanding market access. Recognizing the transformative impact of tokenization on capital efficiency and operational efficiency, the industry must come together to leverage the power of shared infrastructure.
In addition to financial institutions, the broader ecosystem, including technology providers and other players, must collaborate to create a supportive environment. Leveraging standardized processes and protocols to enable interoperability, legal compliance, and efficient platform operations is critical.
Tokenization efforts are currently in their infancy and fragmented, and industry-wide collaboration is urgently needed to address these key issues, combining the robustness of traditional finance (TradFi) with the innovation and agility of DeFi. This strategy will pave the way for a more stable, unified, and mature digital asset ecosystem, balancing technological advancement with regulatory consistency and market stability.
7.3 Promotion
Finally, not only market participants, but governments and regulators also play a key role in promoting responsible growth in the digital asset industry. By developing policies that encourage global trade and support communities (e.g., by creating jobs), they can promote industry development while mitigating risks.
A clear, balanced regulatory framework can foster innovation while guarding against pitfalls that have emerged in the crypto space.
It is also critical to establish public-private partnerships with banks and other financial institutions. These collaborations can accelerate the development of the industry by promoting responsible and sustainable growth.
Through this collaboration, regulators can ensure that growth in the digital asset industry benefits the economy, improves global financial integration, creates jobs, and maintains market integrity and investor protection.
Report link:
Real-world asset tokenisation: A game changer for global trade by Standard Chartered & Synpulse
https://www.hkdca.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/rwa-tokenization-game-changer-global-trade-synpulse.pdf
















