Original article by Derek Edws , Managing Partner, Collab+Currency
Compiled by: Zen, PANews
I am no longer confident that our traditional strategic approaches will be able to address the new realities of the future—especially given the incredible acceleration of artificial intelligence technology and its disruptive potential for the American workforce.
America must begin moving toward a new framework that adapts to the new reality of labor. This starts with understanding two of the most disruptive technological innovations of the past two decades: AI and Crypto.
AI
Thirty years ago, Internet search engines first appeared. Their value was deceptively simple: to retrieve the world's data. Twenty-five years later, OpenAI's ChatGPT has become the fastest-growing consumer app in history. The product has 300 million weekly active users and more than 10 million monthly paying subscribers. In less than two years, the product has an annual revenue of approximately $3 billion.
What is the value of these AI systems? Combining “retrieval” with “completion.” In simple terms:
- Request any job using natural language;
- Leave the completion of the work to computer intelligence.
Over the past three months, we’ve seen clear growth in the ability of these products to complete work requests across a broad range of domains—text, math, audio, video, geometry, programming, and more.
So far, the assumptions for scaling AI systems still hold true: more data, more computing power, and better models. In addition, new dimensions of scaling are being explored, with innovations like test-time compute emerging. Last month, OpenAI’s latest inference model achieved 25% of the performance on cutting-edge math benchmarks that only deep learning mathematicians can solve.
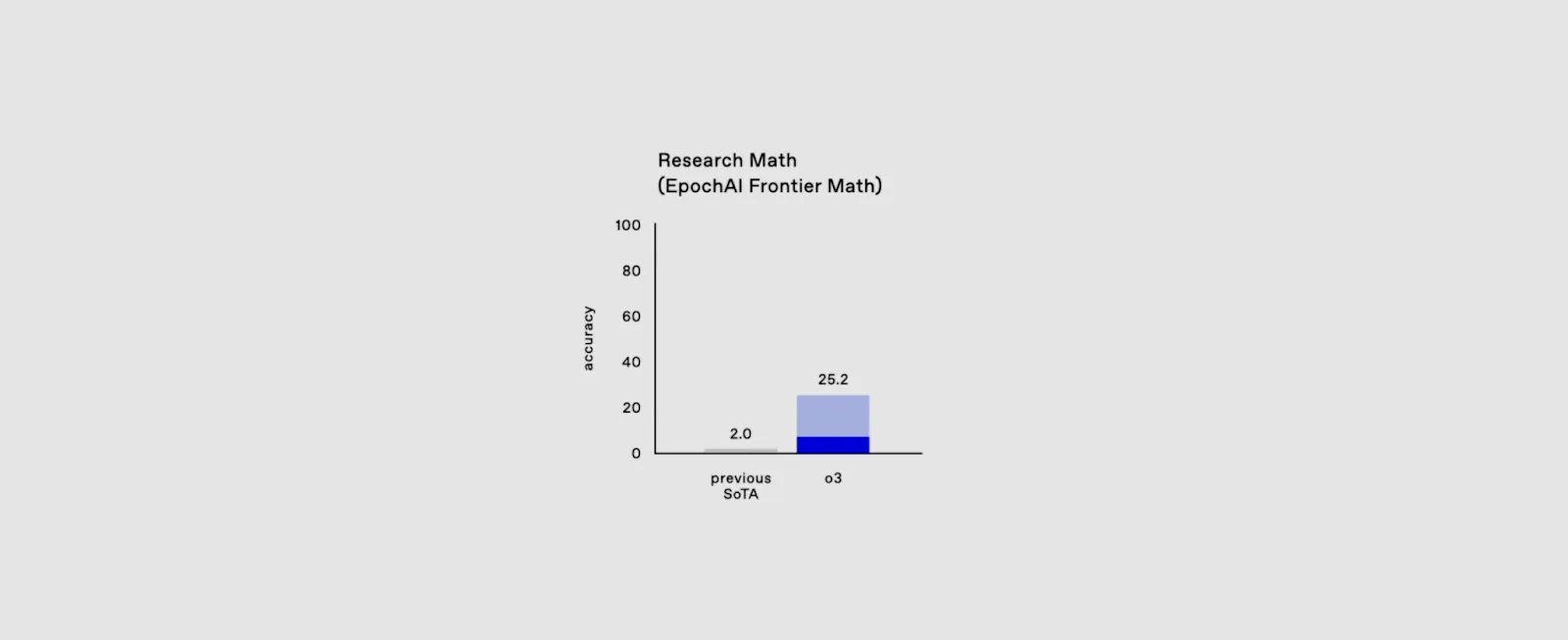
These next-generation reasoning models are adapting to new tasks and producing observable results. At the same time, new advances in robotics are making machines increasingly capable of performing complex physical tasks. Intelligent, human-like hardware will never get tired, never take a vacation, and never go on strike.
This unleashing of technological productivity is not unprecedented—the Industrial Revolution of the 18th century and the Digital Revolution of the 20th century dramatically reduced costs, increased efficiency, and transformed various forms of labor markets and economic structures.
But AI appears to be a different type of technological revolution. These systems are able to create value in unprecedented ways, beyond traditional cost structures. Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei believes that AI could bring us close to 50 to 100 years of biological progress in the next 5 to 10 years, simply by shifting most of our human labor structure to AI systems.
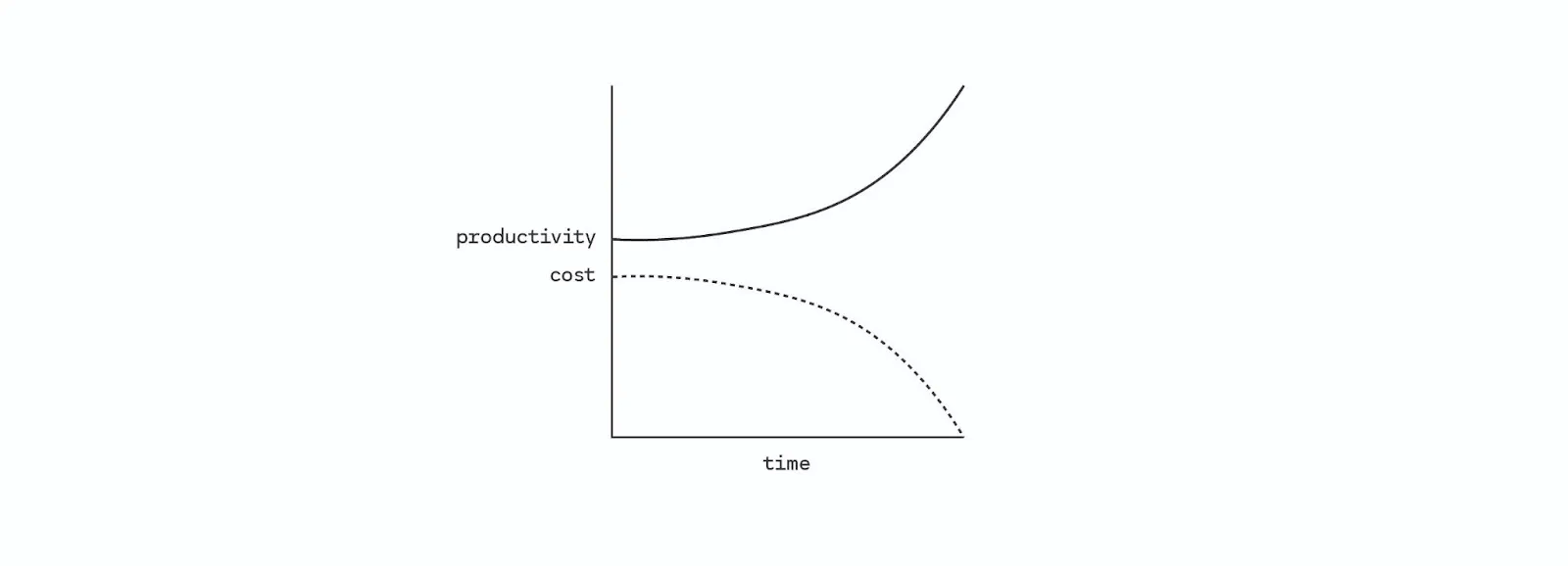
As the infrastructure to support the growth of these systems continues to develop, I believe humanity around the world will see two trend lines emerge:
- The cost of all mental work will converge toward the cost of running an AI system;
- The cost of all manual labor will tend toward the cost of the robot's mechanical parts.
The promise of this technology is clear:
- Unlimited results;
- Prices have been significantly reduced;
- Across every value category.
For the purposes of this article, let’s assume that the above trends hold true. As someone who believes that the next generation of Americans should have the same opportunities as their predecessors, two questions linger on my mind: First, how can the United States win the AI revolution with an advantage? Second, how can individual Americans participate in the benefits of future AI systems and realize their disruptive potential to human labor?
Cryptocurrency
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper, which proposed a new, gamified accounting system in which globally distributed computers could work together to reach a shared digital consensus on the Bitcoin ledger.
Today, Bitcoin is the most powerful supercomputer in the world. The size of the network is far greater than the combined size of the networks of companies such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. However, after fifteen years of development, the blockchain still seems unwieldy:
- Poorly written code may have vulnerabilities that can lead to theft or zeroing out account balances;
- User errors in managing private keys were the biggest cause of cryptocurrency theft last year;
- Compared with traditional web applications, decentralized applications are more difficult to use and have a very high user churn rate.
Despite these limitations, interaction with cryptocurrencies is at an all-time high. One study estimates that 40% of the U.S. population now owns cryptocurrency, compared to 30% in 2023. Around 24,000 developers are actively working on blockchain and blockchain applications each month around the world, up from just 1,000 developers per month a decade ago.
Why are cryptocurrencies growing despite all of these limitations? I believe it’s because cryptocurrencies have five unique characteristics — which work together to be impossible to replicate with any other database architecture:
- Digital ownership . The blockchain database is global, fully auditable, community-owned, tamper-proof, and operates 24/7. Through the blockchain, individuals can own any digital object on the Internet, establishing a global digital property rights system for the first time.
- Coordinate incentives . By automatically executing contracts, blockchain-based protocols can leverage programmable incentives to coordinate new forms of digital work on the network. These incentives can be for those who use a product or service, provide economic security, contribute to core code, provide market supply or demand, recommend others to use the product, etc.
- Frictionless micropayments . Today, most Internet companies must adopt subscription, bundling, and ad-supported business models due to high transaction costs. This limitation constrains innovation in Internet business models and hinders the emergence of consumer-friendly alternatives. Blockchain databases enable frictionless, low-cost digital payments on a global scale - bypassing the inefficiencies of traditional payment systems and without the risk of chargebacks. In addition, any crypto asset can be divided into arbitrarily small units.
- Shared standards . By leveraging shared settlement standards on the blockchain, various protocol tokens, stablecoins, applications, games, and financial services can be seamlessly combined together, just like Lego blocks can be connected at will.
- Distributed security . Blockchain networks are typically distributed across multiple nodes around the world, eliminating single points of failure. This decentralized architecture makes it more difficult for malicious actors to attack these network systems, as they would need to control a majority of the nodes at the same time.
Today, the cryptocurrency economy has a market capitalization of approximately $3.6 trillion and encompasses multiple emerging sectors.
Over the next decade, I believe the crypto economy will be repriced and move significantly higher—driven primarily by two major trends at the intersection of AI and crypto: (1) AI and crypto infrastructure; and (2) AI and crypto applications.
AI and Crypto Infrastructure
To understand the current AI infrastructure landscape, it’s helpful to look back at historical events and draw parallels.
In 1849, the California Gold Rush quickly attracted a large amount of investment. Hundreds of new roads were built for rapid transportation. The port of San Francisco became one of the busiest in the world, shipping prospectors, goods, and tools around the world. A strong banking and financial system emerged to support the needs of the emerging global enterprises. The infrastructure investments at the time laid the foundation for the region's future as an economic powerhouse.
Today, 175 years later, the world is witnessing a similar gold rush, this time with the goal of creating artificial general intelligence (AGI). However, this time the infrastructure to support AI is not limited to a specific region, and these networks of data, computing power, and electricity are being built by competitors around the world.
Unsurprisingly, the capital and computing power required to train, optimize, and deploy AI infrastructure is extremely expensive and only a few companies can afford it. Conservative estimates put the cost of training GPT-3 at over $4 million per instance, and GPT-4 at over $60 million per instance.
More capital, more computing power, better performance.
While I am very proud of and supportive of America’s contribution to AI in the traditional corporate form, I also believe it is important to acknowledge its structural limitations:
- Capturing value . While centralized companies are able to leverage venture capital to drive important AI innovations, the economic benefits of these products are limited to a small number of shareholders, limiting the broader impact on society.
- Proprietary knowledge . Advances in technological frameworks are often concentrated within centralized companies, limiting others’ access to critical breakthroughs — while information now flows 24/7 at internet speeds.
- Opaque systems . Centralizing AI in opaque, closed, centralized systems makes it difficult for independent verifiers to audit company practices around data collection, security, and accountability.
- Closed competition . The huge computing resources required to develop advanced artificial intelligence pose a huge barrier to new products entering the market, and only a few well-funded companies can continue to break through the technical bottleneck.
By combining America’s AI infrastructure with the five unique characteristics of cryptocurrency—digital ownership, aligned incentives, frictionless micropayments, shared standards, and distributed security—I believe we can mitigate the negative effects of centralized AI and restore the competitive spirit that has long defined America’s capital markets. Furthermore, by combining America’s AI infrastructure with cryptocurrency, I also believe this will lead to better performing AI systems with (a) greater transparency and (b) fairer ownership among millions of American participants in the future.
(a) Better performance
To understand the breakthroughs that AI can achieve without a lot of funding, look at the DeepSeek team. Two weeks ago, this research group based in China released DeepSeek-V3, a 670B parameter model that performs comparable to many closed source SOTA models, including GPT-4o and Claude-Sonnet-3.5. DeepSeek has not received any venture capital to date.
As open source projects like Bitcoin and Ethereum have demonstrated, by distributing programmable incentives to a global pool of contributors, it is possible to greatly increase the qualified workforce and computing networks to form a force more powerful than a single lab or centralized system. From this perspective, creating a system that rewards AI labor and computing networks is not much different from creating a system that rewards Bitcoin labor and computing networks.
A few examples:
- For improved training data, encrypted networks can reward humans for contributing high-quality annotated datasets — including private data, proprietary intelligence, or information not available through traditional web scraping.
- For more powerful computing networks, crypto networks can incentivize individuals and organizations to contribute computing power through decentralized marketplaces — quickly building a global network of machines without upfront capital investment.
- For more efficient model training, open source developers can provide customized contributions, improvements, and optimizations to existing models in exchange for corresponding rewards. In addition, when the code and model weights are public, hundreds of researchers and developers can simultaneously publish improvements, debug issues, fine-tune custom models and agents, and create new applications on top of them - all coordinated through the network's incentive mechanism.
Over time, I believe this type of broad collaboration pioneered by decentralized projects like Nous Research, Prime Intellect, and Bittensor will surpass what is possible within well-resourced private companies.
(b) Greater transparency
Open-sourcing AI models allows the research community to fully review their training process, architecture, and behavior, and make improvements. This transparency helps identify potential risks or biases early, leading to more reliable systems that people can trust. By leveraging blockchain in this process, the entire process of creating, rewarding, and improving AI protocols can remain transparent and auditable.
(c) More equitable ownership
Designed for various verticals in the AI technology stack, the crypto network will establish a fairer ownership structure than the existing centralized model. Through programmatic incentives, all contributors and participants in the crypto protocol can be compensated transparently.
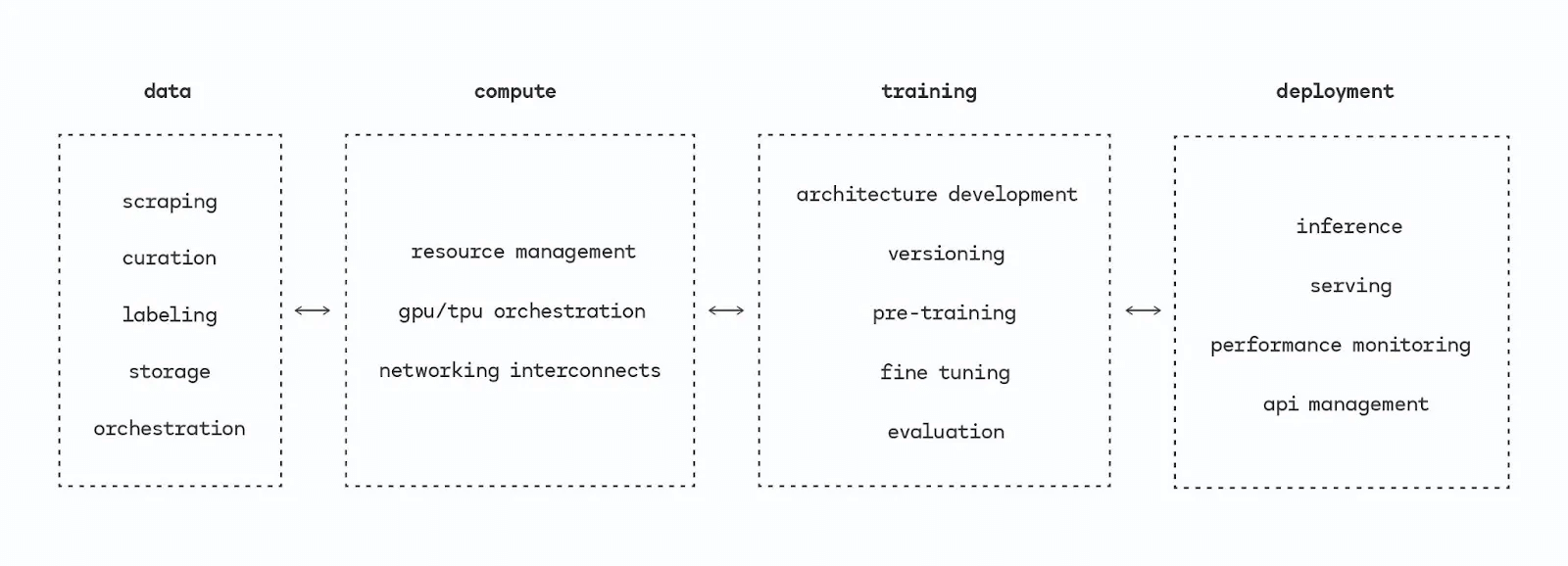
In addition, the entire market formed around various types of work in the AI infrastructure stack will lead to more refined competition in the field of AI design in various categories. Categories and subcategories such as data, computing, training, and deployment can all compete and accrue value in independent environments.
However, it’s not just AI infrastructure that will ultimately benefit. I believe AI agents will completely reorganize the current trajectory of global cryptocurrency adoption — across all application verticals.
AI and cryptocurrency applications
The complexity of cryptocurrency applications has long been seen as a significant barrier to widespread adoption. For the past fifteen years, blockchains have required users to participate in complex approval processes, manage private keys, and understand complex UI patterns that are out of reach for most Internet users.
However, with the advent of agent technology, these user patterns are changing rapidly. If you think of AI models as reactive infrastructure that responds based on previously trained data, then you can think of AI agents as proactive applications that integrate models into new architectures to accomplish narrowly defined goals.
In simple terms, AI agents use underlying models to automatically think, plan, and perform actions. It is important to understand that agents are different from the "robots" we have known in the past. Unlike robots, AI agents can reason on demand. They are able to analyze their own performance, adjust strategies, and solve complex tasks that sometimes require hundreds, and in the future thousands, of unique steps.
In September 2024, I met with one of my portfolio founders who was building an AI agent protocol for blockchain navigation. The protocol was called Wayfinder. Through his phone, using a few simple natural language prompts, I deployed a frontend and token contract that replicated Bitcoin’s monetary policy onto the BASE blockchain, using ETH that was cross-chained from the Ethereum mainnet. The entire process took less than four prompts and a total of five minutes to complete.
Startups like Wayfinder illustrate an important trend: AI agents will mediate the long-standing technical friction of cryptocurrency. In the next 12 months, agents will translate blockchain’s complex structure into seamless natural language interactions, increase protocol accessibility, protect users from their own mistakes, help developers deploy safer code, and significantly reduce consumer churn in complex decentralized products and services.
More importantly, the Key Management Network will extend all of these agent capabilities, allowing agents to seamlessly perform tasks across blockchains without human involvement. The Global Namespace Network will enable each agent’s actions to span all blockchains and be connected to a single human identity.
In simple terms:
Crypto Broker makes it easier to build or use any crypto product, no matter which blockchain it is on.
- In the field of decentralized finance, agents will compress the financial friction of cryptocurrencies into the risk needs of each user by simplifying natural language instructions.
- In the crypto gaming space, agent workflows will power personalized and ownable artifacts in the crypto economy, more complex non-player characters, and on-chain experiences tailored for players.
- In a decentralized organization, humans would agree to overarching policy goals and constraints and allow agents to execute within individual dimensions of business, protocol, or administrative functions.
These guiding roles and advantages bring a revolutionary breakthrough from zero to one for all crypto applications. Millions of new users will join in this way, and no field will be left out.
AI, Cryptocurrency, and Ownership
In understanding the grand trends before us, it is important to look back and remember the lessons of our history. For much of human history, the ability to secure and defend resources meant survival itself. The modern institution of property rights is the product of millions of years of this evolutionary pressure. The concept of property rights is so fundamental to the human experience that it is enshrined in the U.S. Constitution (Fifth Amendment). America’s founding fathers saw property rights as a cornerstone of our system of governance and way of life.
Economists have also long argued that strong property rights are the bedrock of economic growth. They are essential for individuals to be able to securely generate income, store wealth, and use those assets for credit and investment over time.
Several studies support this view. A study of more than 100 countries from 1990 to 2002 showed that countries with stronger property rights grew faster than those with weaker property rights, in part because they were better able to promote technological growth and improved resource allocation.
From the perspective of property rights, blockchain is a core competitive technology. They are the most powerful technological foundation for digital information in the world, enabling immutable record keeping, cryptographically secure ownership, distributed security, and programmatic enforcement of rights through smart contracts.
As the United States enters the era of digital intelligence, blockchain can also serve as a standard environment for all AI infrastructure and applications, ensuring that the United States' AI systems can benefit from the structural support of the five unique characteristics of cryptocurrency. Historically, the United States has created unprecedented opportunities for both individuals and the country - from getting rid of colonial rule, to the constitutional commitment to individual freedom, to fighting against racial segregation, and fierce market competition and entrepreneurship.
Today, standing on the threshold of AGI, I believe the United States has an important opportunity to further solidify its leadership on these same dimensions. Aligning America’s AI policy goals with cryptocurrency will inspire unprecedented levels of individual participation in open source networks, driving incentivized contributions at all levels of the AI stack. Broad participation in our AI marketplace will spur competition and encourage new forms of bottom-up mobilization, leading to broader societal impact.