许多正在学习如何编写智能合约的程序员将学习Solidity语言。有丰富的在线教程和书籍资源,将教我们关于Solidity的内容。当与Truffle框架相结合时,Solidity形成了开发智能合约的“杀手”组合。几乎所有存在于以太坊区块链上的智能合约都是用Solidity编程语言编写的。
在本文中,我们将探讨如何用Vyper编程语言编写智能合约。
主题
介绍设置环境使用Vyper创建智能合约将智能合约部署到 Ganache与智能合约交互与其他智能合约交互以编程方式编译代码
介绍
Vyper是什么?
Vyper是一种面向合约的python编程语言,以以太坊虚拟机(EVM)为目标。Vyper有非常简单/可理解的语法:Vyper的原则之一是使开发人员几乎不可能编写具有误导性的程序。
为什么要用Vyper ?
安全性:在Vyper中构建安全的智能合约应该是可能的。语言和编译器的简单性:语言和编译器实现应该力求简单。可审核性:Vyper代码应该最大限度地让人可读。此外,编写具有误导性的代码应该是最困难的。读者的可读性比作者的可读性更重要,对于没有使用Vyper经验的读者(以及一般没有编程经验的读者)来说,简单性尤其重要。
因此,Vyper提供了以下特性:
边界和溢出检查:对数组访问和算术。支持有符号整数和十进制定点数可判定性:可以计算任何Vyper函数调用的gas消耗的精确上限。强类型小而易懂的编译器代码对纯函数的有限支持:任何标记为常量的东西都不允许改变状态。
设置环境
Vyper需要Python 3.6软件。所以,如果我们没有安装Python 3.6软件,我们必须安装它,然后按照下面的步骤进行:
$ python3 -m pip install --user virtualenv $ pip install vyper $ virtualenv -p python3.6 vyper-venv $ source vyper-venv/bin/activate (vyper-venv) $ pip install vyper (vyper-venv) $ vyper --version
使用Vyper创建智能合约
现在让我们用Vyper创建一个智能合约。首先,我们将创建一个扩展名为.vy的文件,并将其命名为hello.vy,如下:
name: public(String[24])@externaldef __init__(): self.name = "Satoshi Nakamoto" @externaldef change_name(new_name: String[24]): self.name = new_name @externaldef say_hello() -> String[32]: return concat("Hello, ", self.name)
下面是编译vyper文件的方法:
(vyper-venv) $ vyper hello.vy
由此,我们将得到以下输出:

这是智能合约的字节码。要部署智能合约,就需要字节码,但要访问智能合约,需要abi。如何得到abi呢?可以通过以下命令来实现:
(vyper-venv) $ vyper -f json hello.vy
由此,我们将获得以下输出:
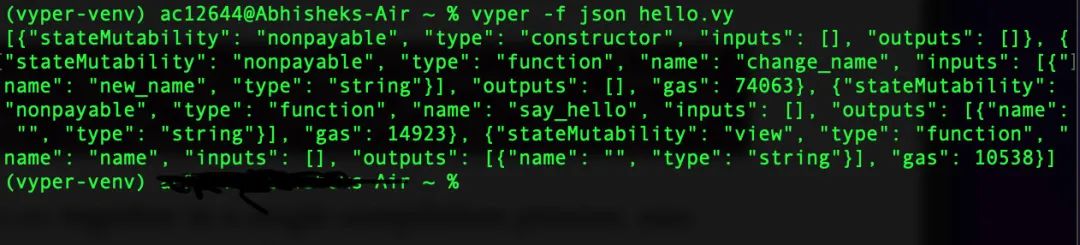
如果我们想在一个编译过程中同时得到abi和字节码,可以在编译过程中合并这两个标志,如下所示:
(vyper-venv) $ vyper -f json,bytecode hello.vy
这将给我们以下输出:

将智能合约部署到 Ganache
那么如何将这个智能合约部署到以太坊区块链中呢?有几种方法可以做到这一点,但让我们用一种熟悉的方法来使用Truffle:
创建一个目录,并使用truffle init初始化它,如下所示:
$ mkdir hello_project $ cd hello_project $ truffle init
设置truffle-config.js如下所示:
module.exports = { networks: { "development": { network_id: "*", host: "127.0.0.1", port: 8545 // port at Ganache running }, } };
创建一个构建目录,如下所示:
$ mkdir -p build/contracts $ cd build/contracts
然后创建一个Hello.json文件,如下所示:
{“abi”: ”bytecode”: }
然后用编译过程的abi或json输出填充abi字段,用编译过程的字节码输出填充字节码字段。需要用双引号将字节码值括起来。不要忘记在abi字段和字节码字段之间放一个逗号。这会给我们一些类似于下面的东西:
{ "abi": [ { "stateMutability": "nonpayable", "type": "constructor", "inputs": [], "outputs": [] }, { "stateMutability": "nonpayable", "type": "function", "name": "change_name", "inputs": [ { "name": "new_name", "type": "string" } ], "outputs": [], "gas": 74063 }, { "stateMutability": "nonpayable", "type": "function", "name": "say_hello", "inputs": [], "outputs": [ { "name": "", "type": "string" } ], "gas": 14923 }, { "stateMutability": "view", "type": "function", "name": "name", "inputs": [], "outputs": [ { "name": "", "type": "string" } ], "gas": 10538 } ], "bytecode": "0x601060e0527f5361746f736869204e616b616d6f746f000000000000000000000000000000006101005260e0806000602082510160c060006002818352015b8260c05160200211156100505761006f565b60c05160200285015160c051850155815160010180835281141561003e575b5050505050506102d756600436101561000d57610252565b60046000601c37600051346102585763e349cb12811861009257600435600401601881351161025857808035602001808260e03750505060e0806000602082510160c060006002818352015b8260c051602002111561006b5761008a565b60c05160200285015160c0518501558151600101808352811415610059575b505050505050005b63b459850381186101ad576101608060208082526000600760e0527f48656c6c6f2c20000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006101005260e06007806020846101200101826020850160045afa5050805182019150506000600181016020836101200101825460c060006001818352015b8260c051602002111561011e5761013d565b60c05185015460c051602002850152815160010180835281141561010c575b50505050508054820191505080610120526101209050818401808280516020018083828460045afa905050508051806020830101818260206001820306601f8201039050033682375050805160200160206001820306601f82010390509050905090508101905090509050610160f35b6306fdde0381186102505760e08060208082528083018060008082602082540160c060006002818352015b8260c05160200211156101ea57610209565b60c05185015460c05160200285015281516001018083528114156101d8575b5050505050508051806020830101818260206001820306601f8201039050033682375050805160200160206001820306601f820103905090509050810190509050905060e0f35b505b60006000fd5b600080fd5b61007a6102d70361007a60003961007a6102d7036000f3"
然后我们可以通过在migrations/2_deploy_hello.js中创建一个新文件来创建一个迁移文件来部署这个智能合约,如下所示:
var Hello = artifacts.require("Hello");module.exports = function(deployer){ deployer.deploy(Hello); };
一切准备就绪后,启动Ganache!
然后,在hello_project目录中,我们可以运行迁移过程,如下所示:
$ truffle migrate
我们会看到类似如下的内容:
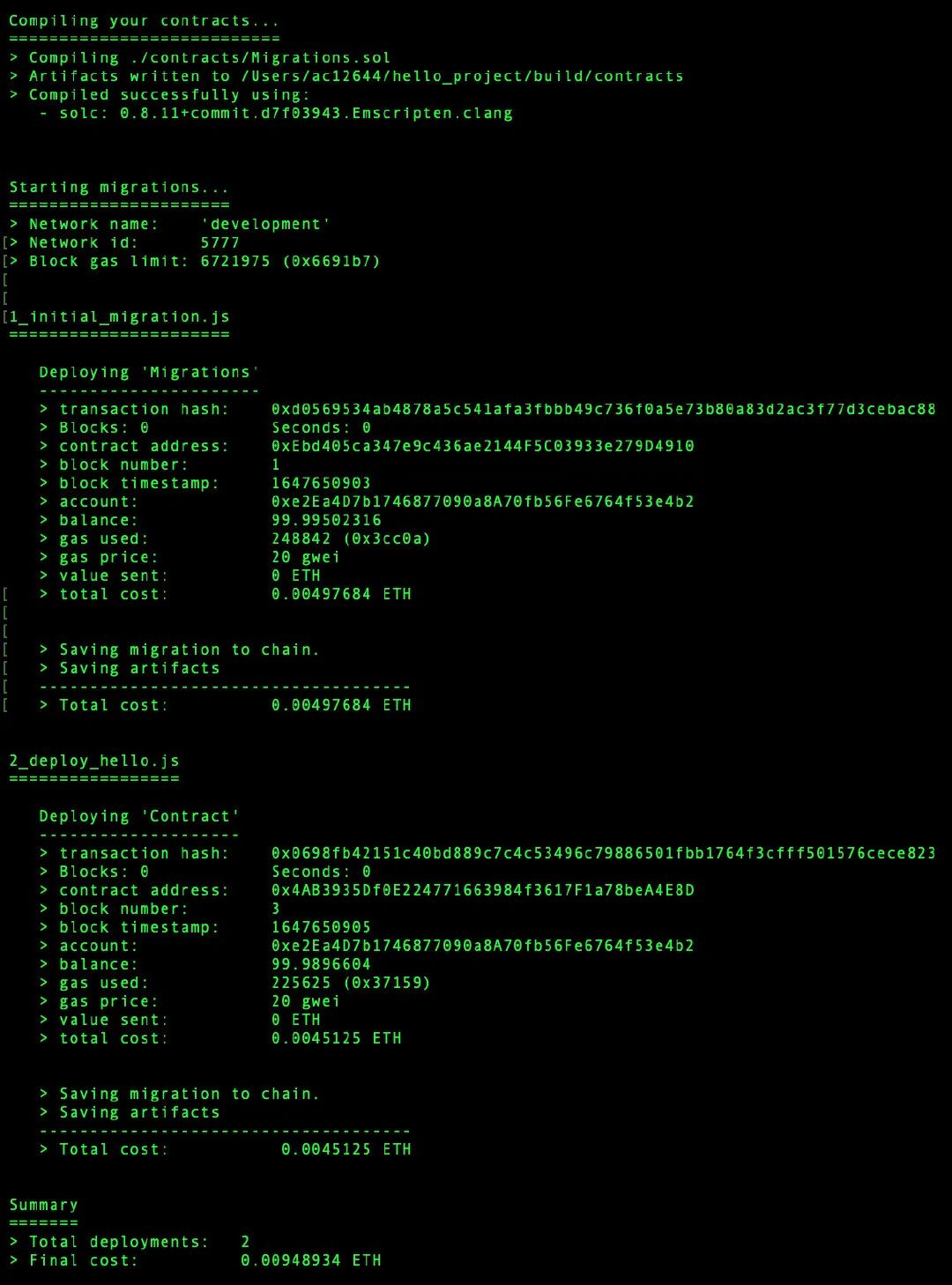
我们用Vyper编写的智能合约已经部署到Ganache。我们的智能合约地址如下:
0x4ab3935df0e224771663984f3617f1a78bea4e8d
与智能合约交互
正如我们之前所做的,我们可以使用Truffle控制台与我们的智能合约进行交互,如下所示:
$ truffle console
我们的智能合约总是被命名为Contract。我们可以使用以下语句访问智能合约:
truffle(development)> Contract.at("0x4AB3935Df0E224771663984f3617F1a78beA4E8D")
我们会得到一个很长的输出,我们可以看到abi,字节码,等等,如下面的截图所示:
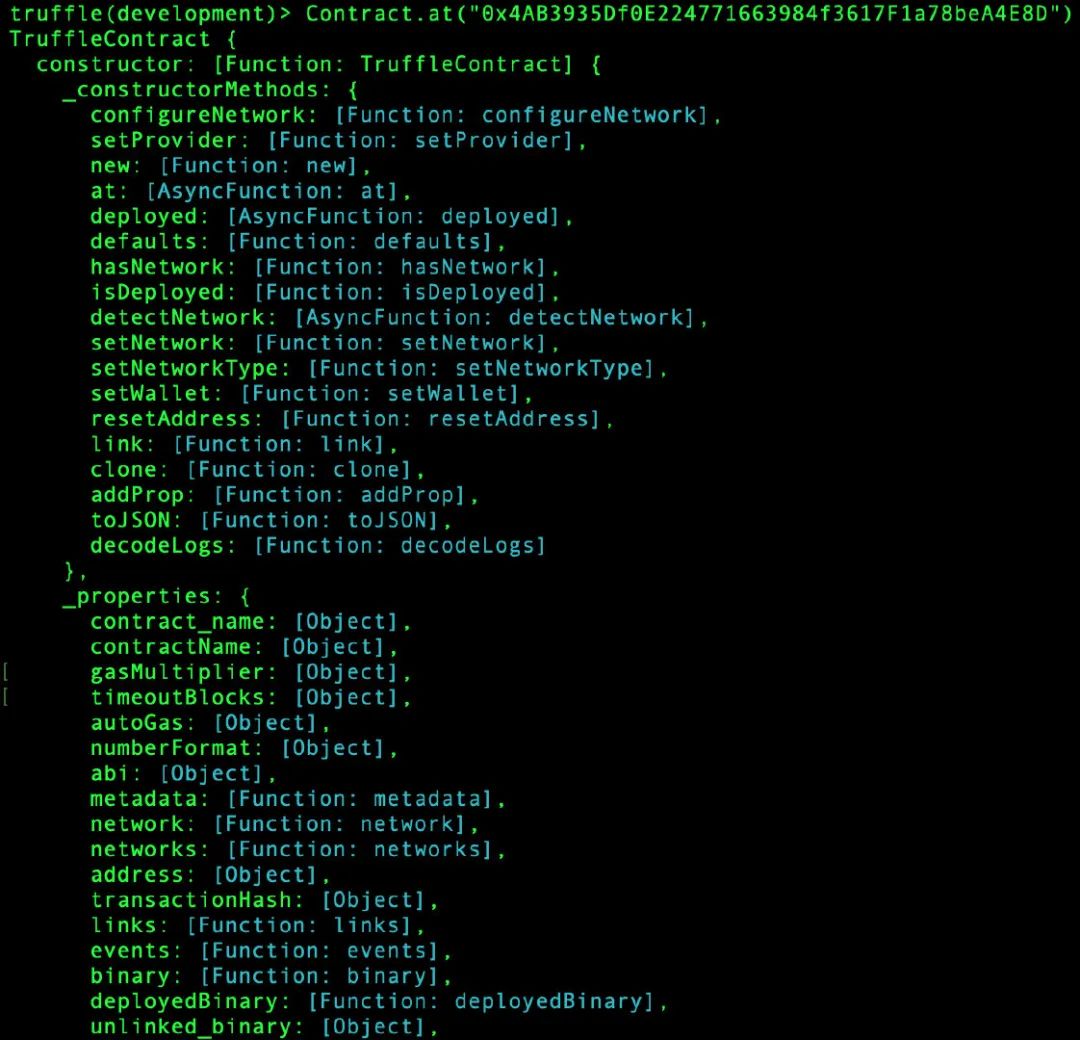
让我们用下面的语句来看看智能合约的name变量的值:
truffle(development)> Contract.at(“0x4AB3935Df0E224771663984f3617F1a78beA4E8D”).then(function(instance){return instance.name.call(); }); "Satoshi Nakamoto"
让我们将名称更改如下:
truffle(development)> Contract.at(“0x4AB3935Df0E224771663984f3617F1a78beA4E8D”).then(function(instance) { return instance.change_name(“Vitalik Buterin”), { from: “0xb28Fc17791bf66719FBFCc65846B01Fe2726e9E2” } });
from字段中的值来自Ganache中的一个帐户。我们只需查看 Ganache 窗口并选择自己喜欢的任何帐户。
输出:
{from: " 0xb28Fc17791bf66719FBFCc65846B01Fe2726e9E2 "}
改名了吗?让我们找出答案。执行如下命令:
truffle(development)> Contract.at(“0x4AB3935Df0E224771663984f3617F1a78beA4E8D”).then(function(instance){return instance.name.call(); });‘Vitalik Buterin’
与其他智能合约交互
我们的智能合约可以与区块链上的其他智能合约交互。
地址数据类型不仅适用于普通账户,也适用于智能合约账户。所以,一个智能合约可以通过捐赠智能合约将以太坊捐献给我们的受赠人!
重启我们的Ganache。还记得hello.vy文件吗?我们想使用自定义名称部署我们的 Hello 智能合约。
我们的迁移文件migrations/2_deploy_hello.js仍然相同,如下代码所示:
var Hello = artifacts.require("Hello"); module.exports = function(deployer){ deployer.deploy(Hello); };
再次编译hello.vy文件以获取接口和字节码。打开我们的合约 JSON 文件,
build/contracts/Hello.json文件。删除所有内容并替换为以下代码:
{ "contractName": "Hello", "abi":
我们必须为智能合约指定一个名称,因为这一次,我们将部署两个智能合约。如果我们不给我们的智能合约一个名称,它将有一个默认名称,Contract。如果我们只想部署一个智能合约,这不是问题。
然后,对于我们的donation.vy,对其进行编辑,并添加以下代码行:
struct DonaturDetail: sum: uint256 name: String[100] time: uint256interface Hello(): def say_hello() -> Bytes[32]:viewdonatur_details: public(HashMap[(address, DonaturDetail)])donaturs: public(address[10])donatee: public(address)index: int128@externaldef __init__(): self.donatee = msg.sender@payable@externaldef donate(name: String[100]): assert msg.value >= as_wei_value(1, "ether") assert self.index < 10 self.donatur_details[msg.sender] = DonaturDetail({ sum: msg.value, name: name, time: block.timestamp }) self.donaturs[self.index] = msg.sender self.index += 1@externaldef withdraw_donation(): assert msg.sender == self.donatee send(self.donatee, self.balance)@externaldef donation_smart_contract_call_hello_smart_contract_method(smart_contract_address: address) -> Bytes[32]: return Hello(smart_contract_address).say_hello()
使用下面的代码,为我们的Donation智能合约创建另一个迁移文件migrations/3_deploy_donation.js:
var Donation = artifacts.require("Donation"); module.exports = function(deployer) { deployer.deploy(Donation); };
编译donation.vy并获取智能合约的接口和字节码。然后,使用以下代码,为我们的捐赠智能合约创建另一个合约 JSON 文件build/contracts/Donation.json:
{ "contractName": "Donation", "abi":
运行迁移。我们可能需要使用——reset,如下所示:
$ truffle migrate --reset
我们将得到以下输出:
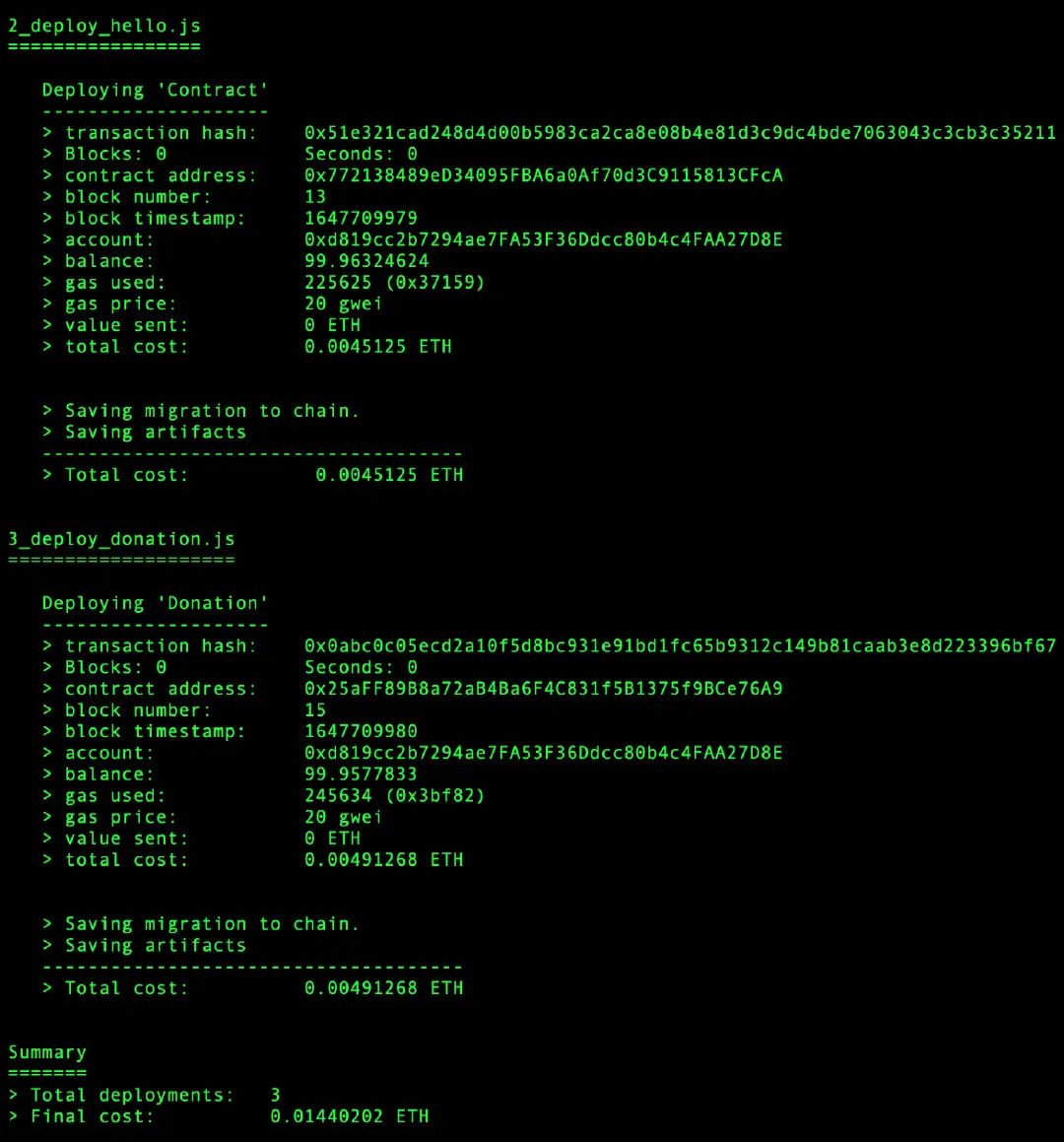
注意Donation智能合约“0x25aFF89B8a72aB4Ba6F4C831f5B1375f9BCe76A9”和Hello智能合约“0x772138489eD34095FBA6a0Af70d3C9115813CFcA”的地址。可能会有所不同。
按如下方式运行Truffle 控制台:
$ truffle console
现在我们的智能合约不再孤单,如下代码所示:
function(instance) {return instance.donation_smart_contract_call_hello_smart_contract_method.call(" 0x772138489eD34095FBA6a0Af70d3C9115813CFcA ");});
输出:
“0x48656c6c6f2c205361746f736869204e616b616d6f746f”
以编程方式编译代码
我们可以创建一个脚本来编译Vyper代码,而不是使用命令行实用程序。确保位于包含Hello.vy和的同一目录中donation.vy。创建一个名为 的脚本compiler.vy,如下:
import vyperimport os, json# You need a Vyper file, the name that you want to give to your smart contract, and the output JSON file. The following code will do this task:filename = "hello.vy"contract_name = "Hello"contract_json_file = open("Hello.json", "w")# Use the following lines of code to get the content of the Vyper file:with open(filename, "r") as f: content = f.read()# Then you create a dictionary object where the key is a path to your Vyper file and the value is the content of the Vyper file, as follows:current_directory = os.curdirsmart_contract = {}smart_contract[current_directory] = content# To compile the Vyper code, all you need to do is use the compile_codes method from the vyper module, as follows:format = ["abi", "bytecode"]compiled_code = vyper.compile_codes(smart_contract, format, "dict")smart_contract_json = { "contractName": contract_name, "abi": compiled_code[current_directory]["abi"], "bytecode": compiled_code[current_directory]["bytecode"]}# The last code is used to write the result to an output JSON file:json.dump(smart_contract_json, contract_json_file)contract_json_file.close()
如果我们使用以下命令执行这个脚本,我们将获得一个Hello.json可与 Truffle 一起使用的文件,如下代码所示:
(vyper-venv) $ python compiler.vy
总结
在本文中,我们了解了如何使用Vyper编程语言编写智能合约。首先,我们安装了Vyper编译器。然后我们开发了一个智能合约。
通过这样做,我们了解了Vyper编程语言的大部分特性,包括函数装饰器、初始化函数和函数权限修饰符。
还有一些数据类型,如地址、整数、时间戳、映射、数组和字节数组(字符串)。我们学习了如何将Vyper源代码编译为智能合约,然后使用Truffle工具将其部署到Ganache中。我们也通过Truffle控制台与智能合约进行交互。
Source:https://medium.com/better-programming/implementing-smart-contracts-using-vyper-a-python-approach-95f9299e64d8


















