By KarenZ, Foresight News
On April 1, the on-chain privacy infrastructure 0xbow announced the official launch of the privacy pool "Privacy Pools" mainnet. Privacy Pools draws on the research results of Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and others, providing Ethereum users with a currency mixing solution that can both protect on-chain privacy and draw a clear line between illegal funds.
This article will introduce the concept, origin, developer team, operating mechanism and potential impact of Privacy Pools on the industry.
What are Privacy Pools?
Privacy Pools is a new type of blockchain privacy tool that aims to provide users with the ability to conduct anonymous transactions while ensuring the compliance of the source of funds.
Unlike traditional currency mixing services (such as Tornado Cash), Privacy Pools can prevent illegal funds from being mixed into the transaction pool while protecting user privacy through the design of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) and Association Set Provider (ASP).
This mechanism not only meets the privacy needs of ordinary users, but also responds to the compliance requirements of regulators, providing a feasible path for the DeFi ecosystem to balance privacy and legality.
Who proposed Privacy Pools? Who published it?
The concept of Privacy Pools originally originated from a research paper co-authored in 2023 by Vitalik Buterin, Jacob Illum (Chief Scientist of Chainalysis), Matthias Nadler (Ph.D. candidate at the University of Basel), Fabian Schär (Professor at the Center for Innovative Finance at the University of Basel), and Ameen Soleimani (Privacy Pools).
This paper explores how to achieve a balance between privacy and compliance on the blockchain, proposes a new privacy-enhancing protocol based on smart contracts, Privacy Pools, and explains how privacy pool technology can act as a neutral infrastructure to enable public blockchains to comply with regulatory requirements across jurisdictions.
The Rrivacy Pools protocol was released by the 0xbow team. 0xbow is a startup project focusing on blockchain privacy and compliance infrastructure. The main team members include:
- Co-founder Zak Cole: also co-founder of BTCFi project corn, managing partner of Number Group and author of EIP-6968.
- Strategic Advisor Ameen Soleimani: Co-founder of Reflexer Finance and IranUnchained, and has worked at ConsenSys, Filter and other companies.
Investors in the project include Number Group, Vitalik, BanklessVC, Public Works and several angel investors.
After the Privacy Pools mainnet was launched, Vitalik and Ethereum core developer Tim Beiko both deposited 1 ETH into the privacy pool to show their support.
How do Privacy Pools work?
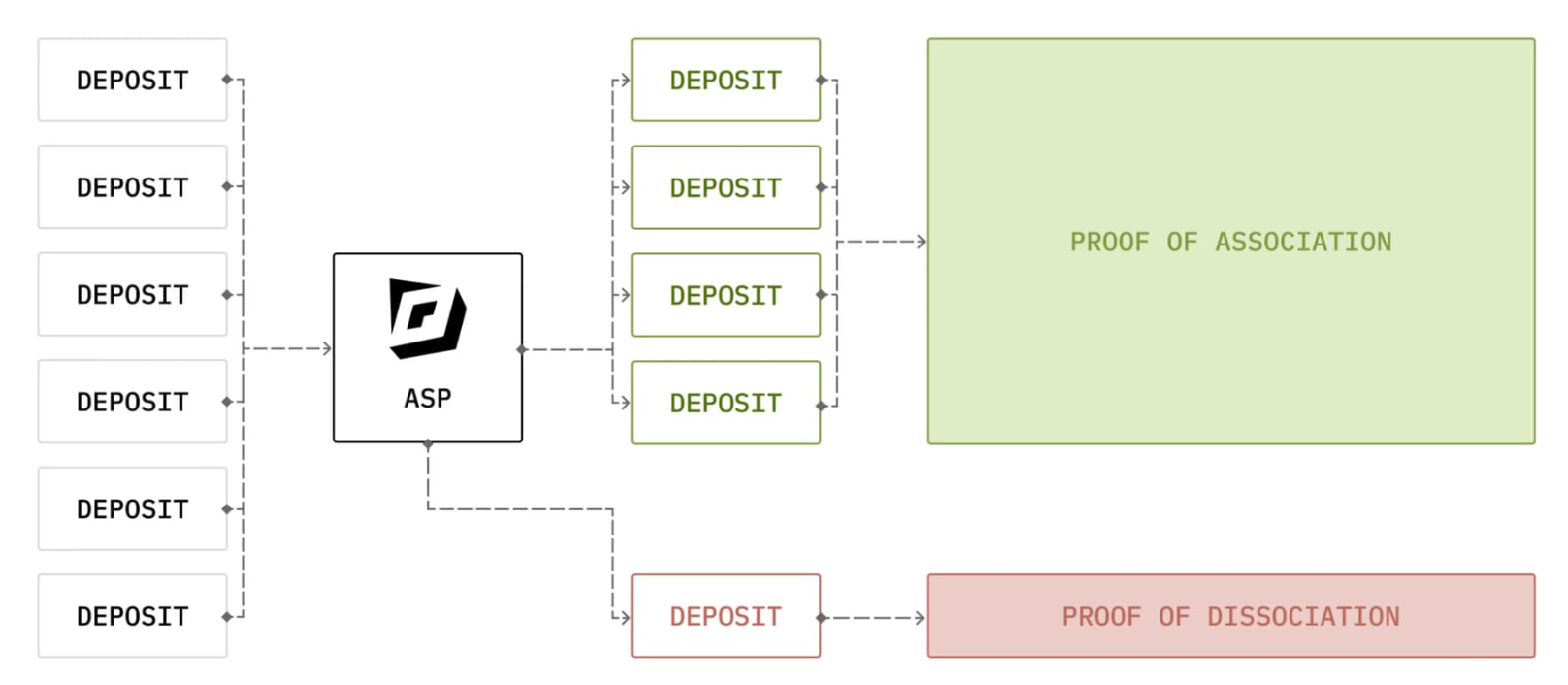
The Privacy Pools architecture consists of a contract layer, a zero-knowledge layer, and an Association Set Provider (ASP) layer. The contract layer manages assets and states, the zero-knowledge layer ensures privacy, and the ASP layer provides compliance functions.
Specifically, utilizing zero-knowledge proofs allows users to prove that they belong to a set of approved depositors without revealing their full transaction history.
The ASP acts as a compliance layer tool, approving deposits that meet predefined criteria and verifying that all private withdrawals come only from approved deposits. The ASP consists of two parts:
1. Service Stack: A set of modular services that continuously monitor, record and classify on-chain activities and assess the trustworthiness of users based on their on-chain behavior.
2. On-Chain Instances: including the Public Registry and the ZKP Verifier. The Public Registry stores and manages ASP data through smart contracts to achieve seamless integration with the blockchain protocol; the ZKP Verifier is responsible for verifying the zero-knowledge proof to ensure that the transaction compliance verification process remains private.
The operating mechanism of ASP is to continuously monitor on-chain transactions and regularly update the "association set". Users can prove that their transactions belong to the compliance set by generating zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) without disclosing specific transaction details. Developers can use ASP to define rule-based access control and screen user qualifications (such as excluding users related to illegal activities), thereby achieving a balance between privacy and compliance.
Privacy Pools allows users to encrypt transactions through a mixing protocol while still being able to prove that their funds come from legitimate sources. The specific operation process is as follows:
- Connecting wallets and creating dedicated wallets: Users connect to the Privacy Pools system through a compatible wallet and create a dedicated 0xbow wallet (this wallet is only used for privacy pools).
- Deposit: Deposit ETH into the privacy pool. The initial version supports a deposit limit of up to 1 ETH and a minimum of 0.1 ETH. After depositing funds, 0xbow ASP will review the source of funds, and if these funds are not from illegal activities, they will be accepted into the associated set. After the transaction is confirmed, the deposited funds become part of the anonymity set. Deposits appear in the Privacy Pools smart contract.
- Withdrawal: Specify the address to receive funds. The dApp will automatically generate a zero-knowledge proof in the user's browser. After confirmation, the withdrawal transaction is completed and the funds are transferred to the specified address.
It’s worth mentioning that since ASPs are constantly updating their rules, initially approved deposits may be disqualified. This means that even if a user passes the initial screening, they may still be barred from making withdrawals.
summary
The launch of Privacy Pools provides users with tools that balance privacy and compliance, and is expected to drive more institutions and companies to adopt blockchain technology.
By isolating illegal funds, Privacy Pools helps to reduce the regulatory pressure on the industry and remove obstacles to the development of the industry to a certain extent. In addition, other privacy protocols can integrate ASP mechanisms to enhance their own compliance and promote the standardization of privacy technology. Of course, ordinary users can also participate in on-chain activities in a safer and compliant manner, redefining the "normal" of blockchain privacy.
However, Privacy Pools still face many challenges on their road to success, including the credibility of ASPs, the centralized review boundaries of ASPs, regulatory adaptability in different jurisdictions, and the attitude of regulators.
References:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4563364
https://docs.privacypools.com/
https://0xbow.io/blog/getting-started-with-privacy-pools