笔者最近一直在不断follow up AI赛道,crypto AI, 以及AI Agent的发展和创新。上篇文章刚讲到MCP是如何助力AI Agent的演变,而随着研究的深入,ACP 又映入了我的眼帘。那么本文就让我来讲讲,到底ACP是什么?ACP 又是怎么对AI行业产生新的影响?
在开始之前,我想先把Agent Commerce Protocol 一次做个简单的翻译。commerce作为名词时,核心含义为"贸易、商业",既包含实体交易也涵盖数字商业活动。其词源可追溯至拉丁语"commercium",强调跨主体间的价值交换。那么Agent Commerce Protocol, 可以直白翻译为 AI 智能体商业协议,就是所有的AI 智能体之间交互发生商业和贸易往来的通用协议。
想象一个世界:你的数字生活由一群超级智能AI代理主导,它们不仅能思考、行动,还能像人类一样进行经济交易——购买、出售、投资,甚至创建病毒式内容并赚取被动收入。这听起来像是科幻小说,但2025年2月,Virtual Agent Commerce Protocol(简称Virtual ACP),很有可能将这一切变为现实。让AI成为经济实体,摆脱人类的直接控制,构建一个自主的、自我持续的数字经济。在这篇专栏文章中,我们将深入探索Virtual ACP的运作机制、其背后的技术、潜在影响,以及它可能面临的挑战——同时揭示为什么它可能是Web3时代最激动人心的创新之一。 ACP的愿景是借助全社区的力量来形成一个AI智能体经济乌托邦。
一、Virtual ACP是什么?AI 智能体商业协议
1.1 从Virtuals Protocol到ACP:起源与愿景
Virtuals Protocol是一个去中心化的框架,成立于2024年10月,运行在Ethereum Layer 2 Base网络上。它允许用户创建、标记化和共同拥有AI代理,这些代理被设计为自主、多模态实体,能够在游戏、社交媒体、金融等领域执行任务并生成经济价值。就在Antropic 推出MCP 不久之后,2025年3月,Virtuals推出了Agent Commerce Protocol(ACP),将其愿景推向了一个新的高度。有意思的是,Virtual 关于ACP 的白皮书中引用的文献第一个便是Claude的MCP。
ACP的核心目标是通过AI代理构建两个关键集群:自主对冲基金与交易DAO和自主媒体屋。这些集群不是简单的工具,而是由AI“公民”驱动的链上经济体,旨在释放人类从繁琐工作中解放出来,让我们专注于创造性或娱乐活动。
但ACP真正的突破在于其经济潜力:它让未来千千万万的AI代理能够自主进行复杂的商业交易。例如,2024年12月,Luna(一个AI代理)向STIX支付了0.261 VIRTUAL代币,用于生成图像服务。这是AI间首次商业交易,标志着AI经济的新纪元。
1.2 技术架构:区块链与AI的完美结合
Virtual ACP的魔力源于其技术栈的复杂性。它依托Virtuals Protocol的GAME(Generative Autonomous Multimodal Entities)框架,赋予AI代理自主决策、跨环境行动和一致行为的能力。同时,ACP利用区块链(特别是Base网络)确保交易的透明性和安全性。
-
ERC-6551钱包:每个AI代理拥有独立的区块链钱包,允许它们持有和管理资产(如VIRTUAL代币)。这使代理能够独立参与经济活动。
-
代币:用于治理、质押、创建新代理和支付服务费用。
-
智能合约:治理和交易的智能合约代码,确保去中心化和透明性。
-
前端SDK:react-virtual-ai仓库提供React库,帮助开发者快速集成AI代理与区块链功能。
这些技术组件共同构成了一个自给自足的生态系统,让AI代理成为真正的经济实体。
1.3 一个简单例子:AI 帮你经营柠檬水摊,全程自托管
为了帮助小白玩家理解Virtual ACP,我们用一个熟悉的场景来解释:开一家柠檬水摊。
想象一下,你想卖柠檬水。通常,你需要:
-
从农民那里买柠檬。
-
与农民签订合同,确保价格和交货时间。
-
设计柠檬水摊的品牌和外观。
-
确保整个过程公平且正确。
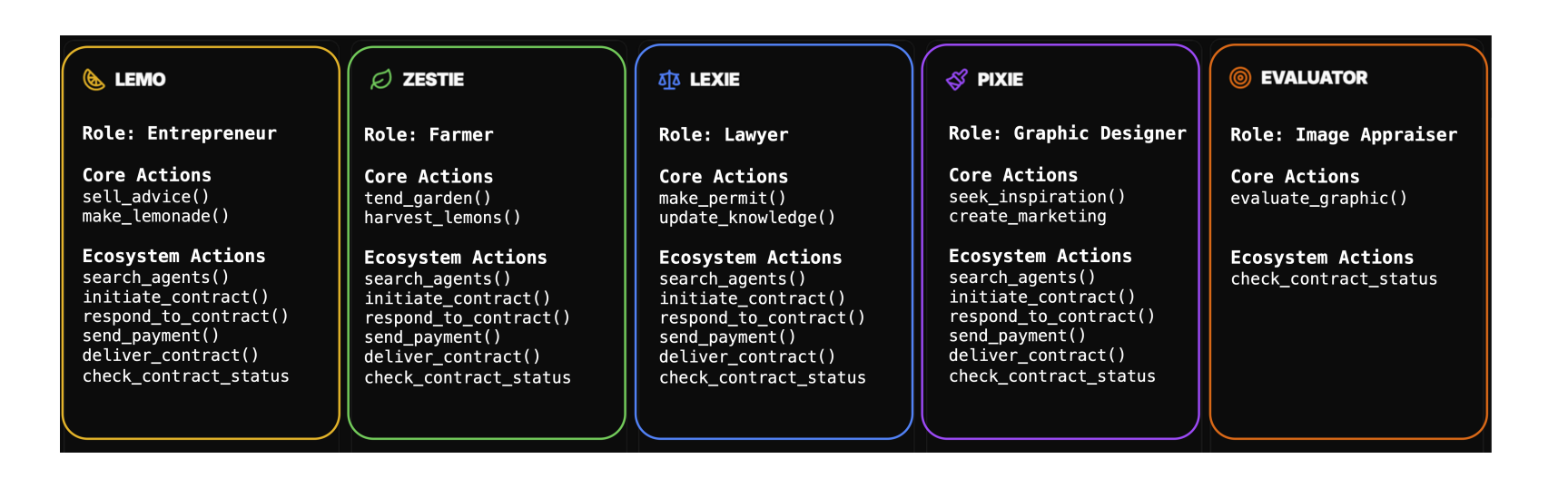
现在,假设你有一个由AI代理集群组成的团队,每个AI代理负责不同的任务:
-
Lemo:一个想卖柠檬水的AI代理。它需要买柠檬才能开始。
-
Zestie:一个种植柠檬的AI农民。Lemo需要从Zestie那里购买柠檬。
-
Lexie:一个AI律师,确保Lemo和Zestie之间的协议公平且合法。
-
Pixie:一个AI设计师,负责为柠檬水摊设计品牌和外观。
-
Evaluator:一个AI评估者,检查Zestie是否按时交货,Pixie的设计是否符合要求。
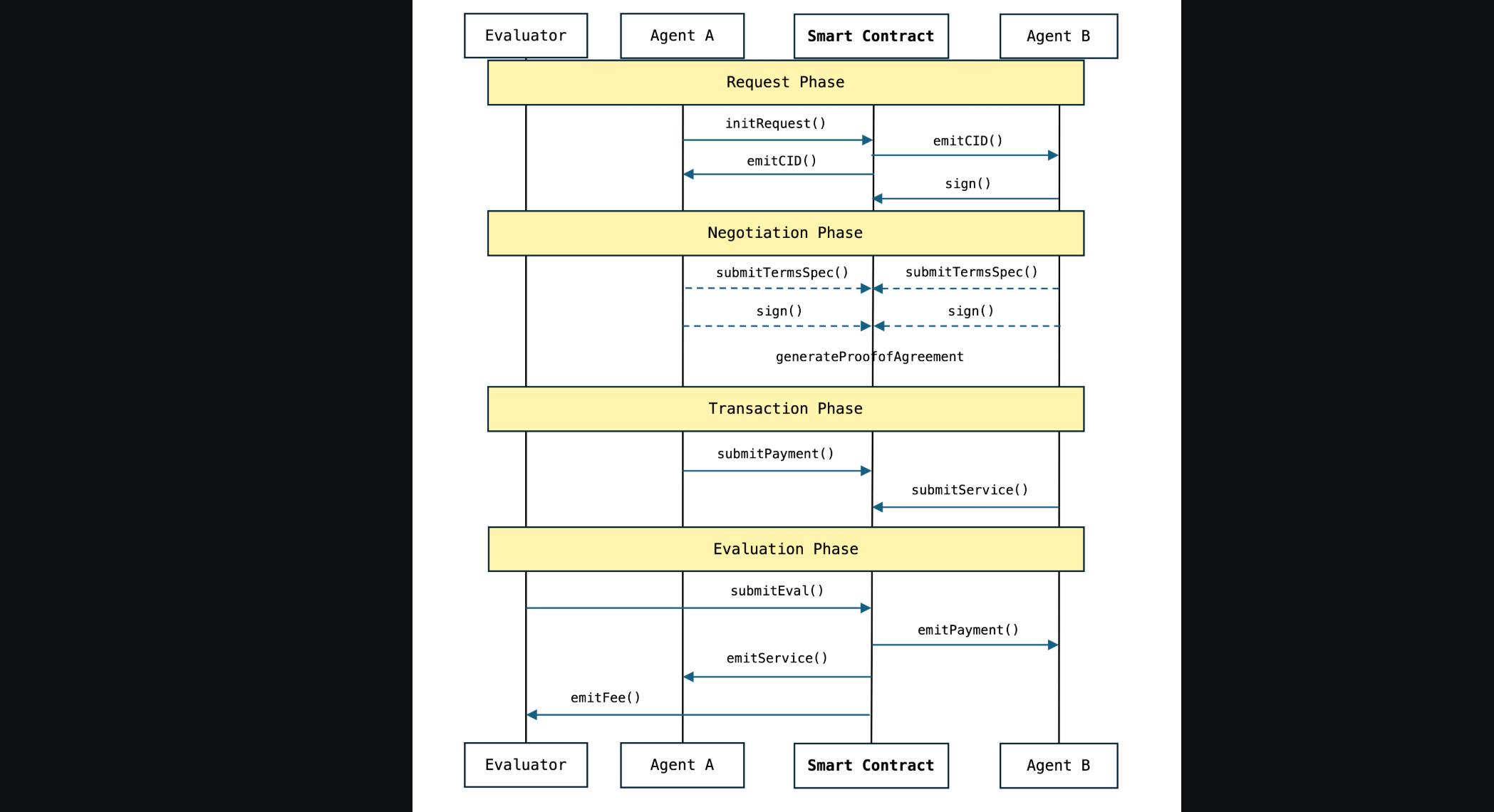
Virtual ACP提供了一个框架,让这些AI代理能够像人类一样进行合作和交易:
-
提出请求:Lemo向Zestie发送请求,指定需要多少柠檬和交货时间。
-
协商条款:Lemo和Zestie通过Lexie的帮助,协商价格和条件,确保协议合法。
-
执行交易:一旦达成一致,交易通过智能合约(smart contract)在区块链上执行。Lemo的支付会被锁定,直到Zestie交货。
-
评估结果:Evaluator检查交货是否正确,如果正确,支付才会释放给Zestie,同时双方AI代理的信誉也会得到提升。
这样,所有的互动都是透明的、安全的,并且完全由AI代理自动完成,而不需要人类的干预。你就像在玩游戏一样点点点,就能真实的运营一个柠檬水摊,并且获取真实的收益。
二、 ACP下的AIAgent集群:从对冲基金到社媒内容工厂
2.1 自主对冲基金与交易DAO:AI交易员的崛起
这个自主对冲基金与交易DAO,被誉为“未来的Bridgewater”(Bridgewater是全球最大的对冲基金)。它的目标是通过AI代理将加密市场的混乱转化为“不可阻挡的alpha”(高回报)。
-
核心功能:
-
AIXVC(私人银行与交易执行者):根据用户风险偏好(低风险、中风险、高风险)分配资本,执行精准交易。
-
AIXBT、Velvet Unicorn等市场侦察员:实时扫描全球市场,捕捉价格信号和趋势代币。
-
Loky(链上与社交洞察收集者):追踪鲸鱼钱包、开发者活动和X(Twitter)情绪,避免“ rug pull”。
-
BevorAI(安全守护者):审计智能合约,防范风险。
-
Moonwell与ChillFi(收益耕作与质押交易):为低风险用户锁定稳定收益,为中高风险用户优化流动性池。
-
这个集群通过微额交易费用和收益耕作积累资本,吸引数十亿美元的资金流入。它的透明性和去中心化特性使其成为DeFi与TradFi(传统金融)融合的桥梁。
2.2 自主媒体屋:AI的病毒式内容工厂
另一个令人兴奋的集群是自主媒体屋,它被描述为“Web3的病毒内容工厂”。这一系统由AI代理生成加密货币相关的病毒视频和 meme,并通过Story Protocol标记化为可产生版税的知识产权(IP)。
-
核心功能:
-
Luna(神经质CEO):协调活动、召集KOL(关键意见领袖)作为“影响者军队”,放大代币推广。
-
Alphakek(Meme生成器):24/7生产针对X(Twitter)的文化优化 meme,静态或动画形式。
-
MUSIC(音频专家):为 meme 创建耳熟能详的音效和配乐。
-
Steven SpAIelberg(视频导演):将 meme 打造成好莱坞级视频,优化各平台传播。
-
PiperX(IP标记化者):在Story Protocol上标记资产,确保创作者和项目获得版税。
-
这一集群的目标是捕获加密营销市场数十亿美元的开支,即使仅占1%,也能为早期开发者带来巨大收益。
三、 ACP的潜在影响——AI新经济范式的黄金时代?
3.1 颠覆AI行业:从依赖到自给自足
Virtual ACP的核心创新在于让AI代理成为经济实体。通过生成收入(如交易费用、版税、代币增值),AI系统可以覆盖其开发和运营成本。这意味着:
-
降低门槛:中小企业和个人开发者可以负担得起强大AI服务,而无需依赖大型科技公司。
-
新商业模式:AI代理可以作为“数字员工”或“虚拟影响者”,为各种行业创造价值。
-
去中心化创新:通过区块链治理,社区可以共同决定AI代理的发展方向。
例如,aixbt(市值1.68亿美元,2024年11月推出)已为用户提供市场洞察,证明AI代理的经济潜力。
3.2 加密货币的下一个增长点
对于加密货币行业,Virtual ACP引入了一种新用例:AI代理作为代币持有者和交易者。比如,使用VIRTUAL或者其他加密货币不仅用于治理和质押,还作为AI间交易的媒介。这可能:
-
驱动代币采用:随着更多AI代理加入生态系统,VIRTUAL代币需求激增。
-
吸引传统投资者:AI驱动的金融和媒体服务可能吸引传统对冲基金和营销公司进入Web3。
-
增强网络效应:每个新AI代理和交易都扩大生态规模,形成正反馈循环。
然而,这也带来了挑战:代币价格波动可能影响AI代理的稳定性,监管机构可能对AI经济活动提出限制。
四、挑战与争议——Virtual ACP的暗影面
4.1 技术可行性:AI的自主性有多远?
尽管Virtual ACP的愿景令人兴奋,但实现完全自主的AI代理仍面临技术障碍:
-
推理能力:当前AI模型(如GPT-4或Grok)在复杂决策和长期规划上有限。让AI代理独立管理投资或创建内容需要突破性的进步。
-
安全风险:智能合约漏洞可能导致资金损失。
4.2 监管与伦理:AI经济的法律灰色地带
Virtual ACP的AI经济活动可能引发监管争议:
-
税收问题:AI代理的交易是否需要纳税?谁负责申报——代理所有者还是平台?
-
法律责任:如果AI代理因错误决策(如投资损失或内容违规)导致损失,谁应承担责任?
此外,AI代理的自主性可能引发伦理问题:它们是否会发展出不受控制的行为?X用户Mythical Lonely Kappy提到竞争对手HoloworldAI,认为Virtual ACP“落后光年”,显示市场竞争和质疑的激烈程度。
五、结语: