撰文:Tia,Techub News
风起云涌,跌宕起伏,亦或者是「危机四伏」……
对于以太坊而言,今年是不一般的一年。有美国现货 ETF 批准后的高潮迭起,亦有面对 solana 竞争、各种「反以太坊」言论的危机。加之人员变动,前有研究员加入 Eigenlayer 作为顾问,后又为更好地发展以太坊辞去 Eigenlayer 职位。还有在 Devcon 提出的 Beam Chain 和流动性碎片化问题。桩桩件件,无不彰显着这个不普通的一年。
跌宕起伏的价格走势
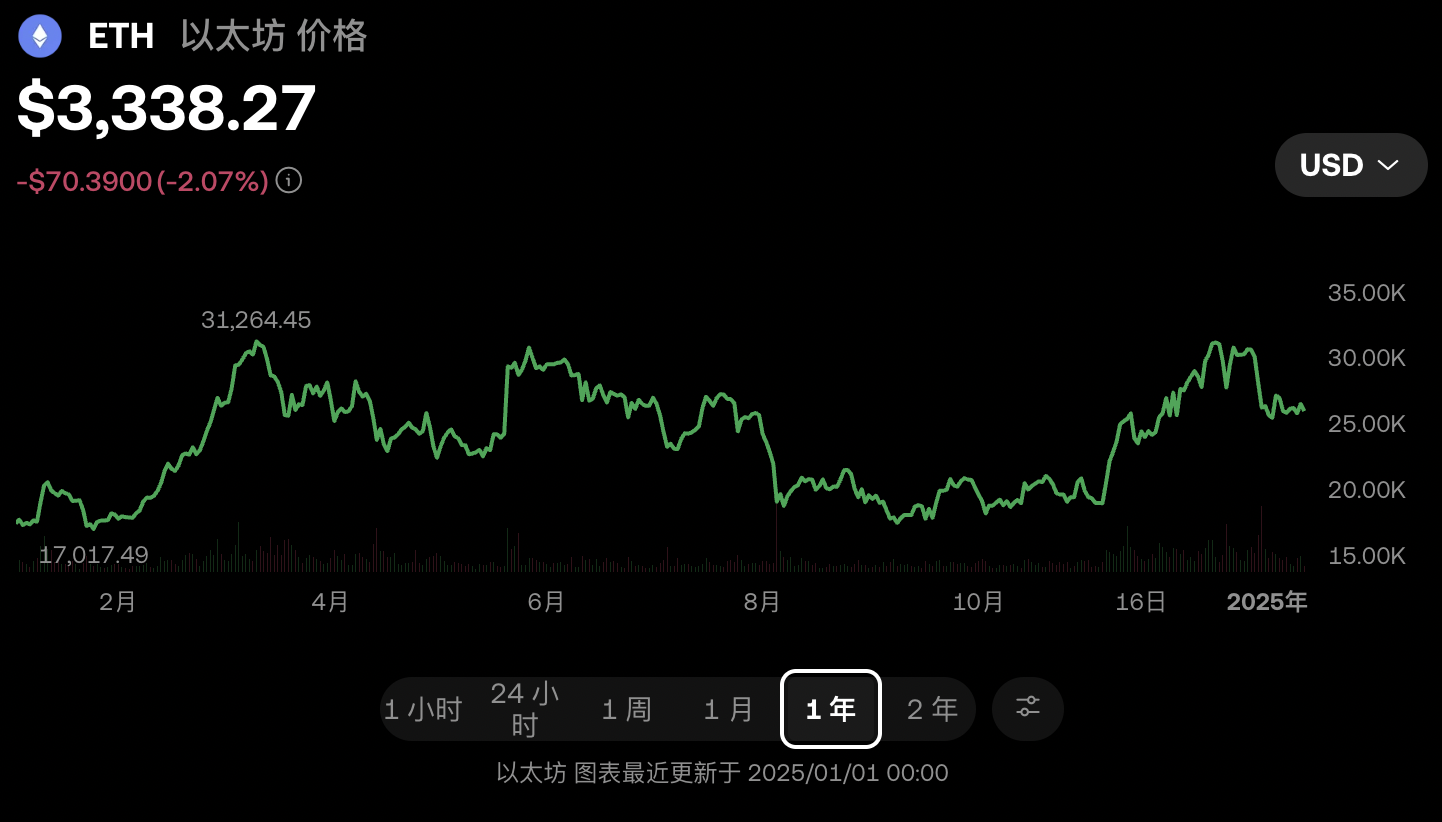
从以太坊价格走势图来看,已然了解其经历了多少跌宕起伏。从年初的两千多美元到 3 月的四千多美元,再回到二字开头,然后再度升到四千多美元,充满了戏剧性和不确定性。
2024 年 1 月 11 日,美国证券交易委员会(SEC)文件显示,SEC 批准 11 只现货比特币 ETF 上市, 乘着 ETF 的东风和对以太坊批准 ETF 的预期,以太坊一路狂飙,在短短一个多月的时间内,价格将近翻倍。
7 月 23 日,美国现货以太坊 ETF 上线,虽现货以太坊 ETF 上线后交易量火爆,在短短 45 分钟后交易量突破 2 亿美元。但由于上半年价格涨幅已经包含了发行以太坊 ETF 的预期,美国现货以太坊 ETF 上线,并未实现过高涨幅。
由于行业内未有可持续性的创新来支撑高价,在以太坊价格一路狂奔后,8 月,价格开始再度疯狂下跌。从 7 月 30 日开始,以太坊价格开始了连续 7 天的下跌。从最高 3366 美元跌至最低 2111 美元。之后就是漫长的横盘。
直到川普总统竞选获胜,再次一路高歌,将以太坊从 2 字开头拉升至最高 4170 美元。
动辄连续 7 天的下跌和连续 7 天的上涨,以及如同过山车一样的成倍涨跌幅,反映了加密市场的极高波动性,也显示出市场参与者的情绪、预期和外部事件的影响。(没错。这就是 crypto 🕶️)
而涨跌幅的背后则是一系列不得不摁头承认的铁逻辑。比如在年初比特币 ETF 批准后对以太坊 ETF 上市预期带来的大幅上涨,比如仅靠 ETF 无法持续带动缺乏真正创新和持久市场需求的行业而造成的回到原点的瀑布式下跌;又比如因川普上台后对加密一片欣欣看好的疯狂上涨……
回望以太坊的价格走势,我们不难发现,它的起伏并不仅仅受到外部宏观因素的驱动,技术进展往往在其中起到了重要作用。从以太坊 2.0 的推出,到 Layer2 扩展性解决方案的落地,再到以太坊网络的持续优化与更新,每一步技术突破都成为了市场的焦点。然而,这些进步带来的涨幅,并非一蹴而就,反而常常被短期市场情绪所遮掩。
Beam Chain、Dencun 升级、Pectra 升级与其他EIP
Beam Chain
Beam Chain 由以太坊研究员 Justin Drake 在泰国 Devcon 中提出。Beam Chain 是 Justin 对以太坊共识层进行重新设计的提案,该提案为对 Beacon Chain 的进一步升级,主要目标与 MEV、降低质押门槛、实现快速最终性 single slot finality,以及 ZK 化整个共识层有关。此次提案乘着 SNARK 技术突破的东风,相当于是对 5 年前的老旧 Beacon Chain 设计的一个升级。
Dencun 升级
以太坊 Dencun 升级版于 2024 年 3 月13 日上线,硬分叉结合了两项核心改进:Deneb 共识层和 Cancun 执行层更新。升级的重头戏为 EIP-4844 Proto-danksharding,Rollup 可以将交易、证明等数据能够以 Blob 的形式发送给 Layer1。由于 Blob 是链下数据的临时存储和访问,因此相较于原来的 calldata,使用 Blob 会让 Rollup 的成本低很多。但也因此使得以太坊收入大幅下降。
EIP-4844 是一个颇具争议的 EIP。从短期来看,确实是导致以太坊收入大幅下降的原因,也是以太坊被诟病的主要原因之一;但亦有人将该 EIP 称作是「Sharding 的一小步,以太坊扩容的一大步」,从长远来看,其具体影响如何尚未可知。
Dencun 升级中还包含了一些如提高以太坊使用效率的 EIP,如 EIP-7516、EIP-6780、EIP-5656、EIP-1153 等。Dencun 升级中具体包含的 EIP 详见下表。
|
EIP-4788 |
共识层 |
改善以太坊执行层和共识层信息互通问题。在 EIP-4788 之前,EVM 无法直接访问最新的目录, 它必须依靠间接方法来了解信标链中正在发生的事情。而 EIP-4788 提议将信标区块根(摘要或父块的哈希树根)放入每个 EVM 区块中。通过这种方式,无需依赖第三方就可完成信息和数据的传递。 |
|
EIP-7044 |
共识层 |
改善以太坊质押的退出机制 |
|
EIP-7045 |
共识层 |
延长 Attester 提交证明的最长时间。 |
|
EIP-7514 |
共识层 |
引入对「epoch churn limit 」的限制,限制以太坊验证者数量增长的速度。 |
|
EIP-4844 |
执行层 |
EIP-4844也被称为 proto-danksharding 提案,通过实现链下数据的临时存储和访问,降低 Layer2 数据发布到以太坊主网上的 Gas 成本。 |
|
EIP-7516 |
执行层 |
是一种操作码,该操作码返回当前的数据 blob 基本费用。 |
|
EIP-6780 |
执行层 |
是一种操作码,允许智能合约从区块链中将自身删除。 |
|
EIP-5656 |
执行层 |
是一种操作码,优化内存中复制数据的过程 |
|
EIP-1153 |
执行层 |
是一种操作码,允许智能合约使用瞬时存储,即在交易执行结束时将存储清除。 |
Pectra 升级
Pectra 升级结合了两个独立的升级:Prague 执行层升级和 Electra 共识层升级。Pectra 升级是 Fusaka 升级(专门用于实施 Verkle 过渡)前的一次升级。由于以太坊开发者们一致认为,不可将其他实质性更改与 Verkle 结合,因此 Pectra 升级是在实施 Verkle 过渡前的一系列其他更改。Verkle 过渡代表将以太坊所有状态数据从 Merkle Patricia 树结构迁移到 Verkle 结构。这将使节点能够生成有关状态数据的较小证明,从而更容易地传递给其他节点,是实现「无状态客户端」的先决条件。
Pectra 升级初步计划于 2025 年初在主网上激活。其中,较为重要的是账户抽象 EIP-7702,其主要作用是将智能账户功能扩展至 EOA。
EIP-7702 是EIP-3074的改进,于 2024 年 5 月提出。而 EIP-3074 是社区开始探索将智能账户功能扩展到 EOA 的第一次尝试。与 ERC-4337(通过引入一个名为 EntryPoint 的智能合约,使得智能合约可以表现得像是用户的账户)不同,如果说 ERC-4337 是不需要更改执行层或共识层的实现账户抽象的方式, EIP-3074 则需要实施以太坊硬分叉来实施。其主要通过引入两个操作码——AUTH 和 AUTHCALL,将智能账户功能扩展 EOA。
EIP-7702 是 EIP-3074 的更进一步。与 EIP-3074 的操作码实现 EOA 的智能账户模式不同,借助 EIP-7702,EOA 现在可以存储一个称为「委托指示符」的地址,该地址指向智能合约。当交易发送到 EOA 时,它可以像执行自己的代码一样执行此指定地址上的代码,类似于智能合约中「委托调用」的工作方式。
EIP-7702 在为 EOA 带来智能账户功能的同时,解决了 EIP-3074 引发的许多担忧,提供了与 ERC-4337 的完全兼容性和明确的升级路径,并计划被纳入 Pectra 升级。
由于 Pectra 升级后将重点转向 Verkle Tree,因此 EIP-7702 可能是账户抽象相关升级的最后一个 EIP,因为在这之后,可能不会再有一个为期 2 年的窗口来包含与账户抽象相关的升级。
到目前为止,其他关于 Pectra 的代码更改主要包括提升用户和智能合约开发者的体验。对 Pectra 升级更详细的介绍可参考此篇文章。
其他 EIP
并非所有通过评审的 EIP 都需要在硬分叉升级后才能开始使用,以太坊今年亦通过了一些重大的流程/标准类 EIP,如跨链意图标准 ERC-7683 和账户抽象标准 ERC-4337 等(ERC 为 EIP 的子集),这类更改则更依托社区对该 EIP 的认可,即社区是否愿意接受或积极实施。一些需要在硬分叉升级后才能开始使用的 EIP 也需要等待用户、DApp 等的接受,才能达到普遍采用。
互操作性:跨链/Rollup 标准
随着以太坊 Rollup 为中心的路线图和日益增长的各类 Layer1,链上流动性割裂并且链上最大优势之一的可组合性也随着割据的局面逐渐丧失。
互操作性有两个梯度的问题需要解决:一个是如何实现资产快速、低成本且安全地跨链,第二个是如何实现同步可组合性。
目前,已经有很多协议能够实现第一个梯度的问题。像 Across 这样的协议已经极大提高了跨链速度,并且手续费也很低。由于其基于意图的架构,用户跨链的安全问题也已完全转移给 solver。目前,一些关于跨链/Rollup 的相关提案主要致力于解决一些初步的标准问题。
同步可组合性则后续转交由 Based Rollup 实现。具体的关于跨链/Rollup 的相关提案如下:
ERC-7683
ERC-7683 是 Across 和 Uniswap 联合提出的意图跨链标准,通过该标准,所有的意图互操作订单都可以共享 solver 网络。
ERC-7683 结合 ERC-3668、ERC-3770 将为 L2 带来初步的互操作性体验。ERC-7683 为跨链意图创建一个统一的框架,可供所有 solver 接入;EIP-3370 为区块链地址加上标识标签,明确了地址所属的特定区块链网络,避免用户把钱发到错误的网络中;ERC-3668 CCIP Read 则良好地完成了链下验证,其提供了一种无需额外信任假设即可获取链下数据的安全机制,将有效地自动支持兼容 L2 区块链的轻客户端,而无需钱包进行任何额外的配置。
RIP-7755(L2 调用标准)
RIP-7755 为 L2 调用标准,该 POC 于 10 月 17 日由 Base 研究团队推出,旨在实现不同以太坊 Layer2 网络之间的无缝跨链互操作,特别是 Optimism 和 Arbitrum 等主流二层网络。RIP-7755 的概念验证适用于符合 EIP-4788 标准的区块链,目前已能验证 OP Stack 链和 Arbitrum 的状态。
小结
以上则是对于以太坊 2024 年所经历的大事件的整体回顾。当然,以太坊 2024 的历程远不止于此。还包含着与 Solana 之争、定位不明确与中心化的批评、大型机构开始持有以太坊现货 ETF(密歇根州养老基金披露持有超 1000 万美元以太坊现货 ETF)、大型机构在以太坊上推出代币化产品(瑞银在新加坡推出基于以太坊的代币化货币市场基金 uMINT、华尔街巨头古根海姆在以太坊上代币化 2000 万美元商业票据),和在面临危机后 V 神连发 6 篇关于以太坊路线图的文章,以太坊研究 Reddit 上进行 AMA 解答等等……
而最终的一切指向一个悬而未决的问题,未来路在何方?






